* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download fighting disease
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
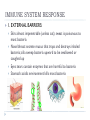
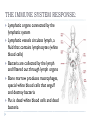
FIGHTING DISEASE SBI 3C: OCTOBER 2012 DISEASE: Pathogen: A disease causing microorganism Pathogenic bacteria produce toxins once they enter your body Toxins are harmful to human hosts, especially since they can travel easily through your circulatory system IMMUNE SYSTEM RESPONSE 1. EXTERNAL BARRIERS: Skin: almost impenetrable (unless cut); sweat is poisonous to most bacteria Nose/throat: secrete mucus that traps and destroys inhaled bacteria; cilia sweep bacteria upward to be swallowed or coughed up Eyes: tears contain enzymes that are harmful to bacteria Stomach: acidic environment kills most bacteria THE IMMUNE SYSTEM RESPONSE: Lymphatic organs connected by the lymphatic system Lymphatic vessels circulate lymph, a fluid that contains lymphocytes (white blood cells) Bacteria are collected by the lymph and filtered out through lymph organs Bone marrow produces macrophages, special white blood cells that engulf and destroy bacteria Pus is dead white blood cells and dead bacteria ANTIBODY FORMATION: Antibodies are protein molecules that inactivate invaders by binding to them Humans contain more than 10 million different antibody types TYPES OF IMMUNITY: Active Immunity: Passive Immunity: Lasting protection against an invader through the manufacture of antibodies (ie. previous infection, some vaccinations) Temporary protection against a particular disease by the direct introduction of antibodies (ie. mom to baby, vaccinations) Vaccine: Dead or weakened bacteria; body reacts to create to antibodies