* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
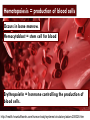
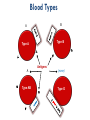
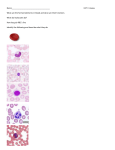
Erythrocytes Platelets Leukocytes Separation of Blood Components Centri = center Centrifuge activity: vial, pencil, string, dirty water Buffy Coat Pg 299 Leukocytes = white blood cells immunity Platelets = clotting Buffy Coat The layer produced by these two types of blood elements is called the “Buffy Coat.” http://adam.about.com/care/Blood-clotting-animation.htm Pg 299 Leukocytes: Buffy Coat Leuko = white Cyte = cell 1. Neutrophils = phagocytes 2. Eosinophils = kills worms, fights allergies, neutralizes harmful chemicals 3. Basophils = contain histamine to fight allergies and inflammation. http://adam.about.com/care/Blood-clotting-animation.htm Pg 299 Leukocytes: 4. Lymphocytes = immunity B-cells: produces antibodies T-cells: fights tumors and viruses and activate B-cells Pg 299 Leukocytes: 5. Monocytes = phagocytes that become macrophages “Clean-up Team” = digests larger cells. Mono = one Pg 299 Erythrocytes = red blood cells (RBCs) carries oxygen Hemoglobin = part of erythrocyte that bonds to carries the oxygen and also can transport CO2 waste away erythro = red Occurs in bone marrow. Hemocytoblast = stem cell for blood Erythropoietin = hormone controlling the production of blood cells. http://health.howstuffworks.com/human-body/systems/circulatory/adam-200028.htm BLOOD Blood cells have antigens and antibodies. Antibodies are what the cell doesn’t like (which is anything different from the “type.”) Antigens are tiny receptors on the outside of the blood cell that matches the “type.” Blood Types A B Type A Type B Antigens A Type AB (none) Type O Genetics of Blood type phenogenotype type A B AB O antigen on RBC antibodies in blood donation status AA Ai type A antigens on surface of RBC anti-B antibodies Receive A or O or BB B i type B antigens on surface of RBC anti-A antibodies Receive B or O AB both type A & type B antigens on surface of RBC no antibodies universal recipient ii no antigens on surface of RBC anti-A & anti-B antibodies universal donor or Rh comes from the rhesus monkey in which the factor was originally identified. Rh+ means the RBCs carry the Rh antigen. If an Rh- person receives Rh+ blood, their immune system will react to the transfusion and the patient’s antibodies will attack and kill the new blood cells. How could an Rh+ woman became pregnant with an Rhbaby and what would happen to the baby? Bleeding Disorders Thrombocytopenia = not enough platelets to clot. Liver can’t produce clotting factors due to lack of Vitamin K. Hemophilia = several inherited bleeding diseases “Free bleeder” No platelets are present. http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=96AC672C-54E2-43D0B6FE-9D4B5C0500C4&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US