Molecular Genetics of von Willebrand Disease
... from the midportion of vWF identified not only the authentic gene on chromosome 12 but a second sequence on chromosome 22.12 The latter has recently been localized to 22q11.22-ql 1.23.49The complete exon/intron structure of the vWF gene has been established by Mancuso et al.”)The 52 exons span 178 k ...
... from the midportion of vWF identified not only the authentic gene on chromosome 12 but a second sequence on chromosome 22.12 The latter has recently been localized to 22q11.22-ql 1.23.49The complete exon/intron structure of the vWF gene has been established by Mancuso et al.”)The 52 exons span 178 k ...
Coronary sinus blood sampling: an insight into Review
... tissues.23 Each of these mechanistic processes can contribute to a variable extent in individual coronary patients and each might be better defined by regional rather than generalized blood sampling. ...
... tissues.23 Each of these mechanistic processes can contribute to a variable extent in individual coronary patients and each might be better defined by regional rather than generalized blood sampling. ...
Conference Abstracts - Canadian Society for Transfusion Medicine
... Polymer-Mediated Immunocamouflage of Allogeneic Lymphocytes Induces Tolerance via Generation of Functional Regulatory T Cells and a Decrease in CD8+ T cells .................................................... 106 Pooling Components for Exchange Transfusion .......................................... ...
... Polymer-Mediated Immunocamouflage of Allogeneic Lymphocytes Induces Tolerance via Generation of Functional Regulatory T Cells and a Decrease in CD8+ T cells .................................................... 106 Pooling Components for Exchange Transfusion .......................................... ...
Too Many Periods
... She began bleeding again three days ago and describes it as “heavy.” She is passing clots. She is feeling weak, and feels dizzy when she stands up too quickly. She has been changing pads every ½ to 1 hour. She is also complaining of significant cramping somewhat relieved by ibuprofen. Her menarche o ...
... She began bleeding again three days ago and describes it as “heavy.” She is passing clots. She is feeling weak, and feels dizzy when she stands up too quickly. She has been changing pads every ½ to 1 hour. She is also complaining of significant cramping somewhat relieved by ibuprofen. Her menarche o ...
A WOMAN WITH SPORADIC HEMOPHILIA
... an open flap and a cauterization to stop the bleeding has been applied. She was the third child of 7 children in the family, 3 of them were man with normal life and 4 women also have no history of bleeding. Her parent and grand-parent were all dead because of aging problems. She also has 2 sons with ...
... an open flap and a cauterization to stop the bleeding has been applied. She was the third child of 7 children in the family, 3 of them were man with normal life and 4 women also have no history of bleeding. Her parent and grand-parent were all dead because of aging problems. She also has 2 sons with ...
Association Bulletin #14-02 - TRALI Risk Mitigation for
... Following Blood Collection and Transfusion” for fiscal year 2010 stated that TRALI fatalities attributed to plasma transfusion had declined by 83% from a peak of 23 cases in 2006 (preTRALI risk mitigation) to four cases (post-TRALI risk mitigation) in 2010. 5 The low risk of TRALI-related fatalities ...
... Following Blood Collection and Transfusion” for fiscal year 2010 stated that TRALI fatalities attributed to plasma transfusion had declined by 83% from a peak of 23 cases in 2006 (preTRALI risk mitigation) to four cases (post-TRALI risk mitigation) in 2010. 5 The low risk of TRALI-related fatalities ...
Effect of whole blood viscosity and red cell mass on
... phase act as a “spark,” which, if large enough and sustained enough, drives the process into the amplification step. The thrombin generated in initiation can activate fXI, create more fVa to complex with fXa, cleave VIII from vWF and activate it, and can activate fIX. The fXa/fVa prothrombinase comp ...
... phase act as a “spark,” which, if large enough and sustained enough, drives the process into the amplification step. The thrombin generated in initiation can activate fXI, create more fVa to complex with fXa, cleave VIII from vWF and activate it, and can activate fIX. The fXa/fVa prothrombinase comp ...
FIBRINOGEN AN INFORMATION BOOKLET
... is triggered. Several proteins, called coagulation factors, go into action to produce thrombin. The thrombin then converts fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin produced from fibrinogen is the main protein in a blood clot. It surrounds the cells in the blood and plasma and helps form the clot. The resulting ...
... is triggered. Several proteins, called coagulation factors, go into action to produce thrombin. The thrombin then converts fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin produced from fibrinogen is the main protein in a blood clot. It surrounds the cells in the blood and plasma and helps form the clot. The resulting ...
as a PDF
... enzymatic activity known as ‘tenase’, a nickname for the enzymatic activity that acts on factor X. Activation of factor X to factor Xa by the extrinsic or intrinsic pathways is the start of the common pathway of coagulation. The latter pathway is thought to be of little significance in vivo since pa ...
... enzymatic activity known as ‘tenase’, a nickname for the enzymatic activity that acts on factor X. Activation of factor X to factor Xa by the extrinsic or intrinsic pathways is the start of the common pathway of coagulation. The latter pathway is thought to be of little significance in vivo since pa ...
Hemophilia in the Neonate
... • FVIIIc is final component of Intrinsic Pathway and along with activated Factor IX activates Factor X within the Common Pathway • Plasma levels of FVIIIvW are WNL – Female carriers and male fetuses in utero have FVIIIc/FVIIIvW ratio less than 1 (nl ratio is equal to 1) ...
... • FVIIIc is final component of Intrinsic Pathway and along with activated Factor IX activates Factor X within the Common Pathway • Plasma levels of FVIIIvW are WNL – Female carriers and male fetuses in utero have FVIIIc/FVIIIvW ratio less than 1 (nl ratio is equal to 1) ...
Bleeding in ACS Patients - Virginia Commonwealth University
... Risk factors for bleeding were identified using logistic ...
... Risk factors for bleeding were identified using logistic ...
ABO Blood Groups and Cardiovascular Diseases
... homozygous A2 and A2-O combinations, were associated with increased thrombotic risk when compared to OO genotypes. The relative thrombotic risk of AB genotypes and A1-combinations was increased by 90–110% when compared to OO genotypes and the relative thrombotic risk of the homozygous B genotype and ...
... homozygous A2 and A2-O combinations, were associated with increased thrombotic risk when compared to OO genotypes. The relative thrombotic risk of AB genotypes and A1-combinations was increased by 90–110% when compared to OO genotypes and the relative thrombotic risk of the homozygous B genotype and ...
The Complete Blood Cell Count (CBC) Part 1: The Hemogram
... Prerequisites for this Post-Test are the tutorials for Blood Cell Morphology and the CBC (Part1, Part 2, and Part 3). There are 100 items presented in the format of incomplete statements. Four or more suggested completions are given for each item. Select the one response that MOST correctly complete ...
... Prerequisites for this Post-Test are the tutorials for Blood Cell Morphology and the CBC (Part1, Part 2, and Part 3). There are 100 items presented in the format of incomplete statements. Four or more suggested completions are given for each item. Select the one response that MOST correctly complete ...
Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus capitis strains isolated from
... disinfection and first aliquot diversion. The majority of PC contaminants are commensal skin flora introduced by venipuncture at the time of blood collection. The predominant organisms are Grampositive coagulase-negative staphylococci such as Staphylococcus capitis. This bacterium has been implicate ...
... disinfection and first aliquot diversion. The majority of PC contaminants are commensal skin flora introduced by venipuncture at the time of blood collection. The predominant organisms are Grampositive coagulase-negative staphylococci such as Staphylococcus capitis. This bacterium has been implicate ...
Full Text - Maastricht University Research Portal
... anticoagulant proteins (e.g. AT,18 PC,19 or PS deficiency20,21) or gain-of-function mutations in coagulation factors (FV Leiden [FVL]22 and prothrombin G20210A23). Most important environmental risk factors are aging, immobilisation, surgery, cancer, and in women also pregnancy and hormonal contracep ...
... anticoagulant proteins (e.g. AT,18 PC,19 or PS deficiency20,21) or gain-of-function mutations in coagulation factors (FV Leiden [FVL]22 and prothrombin G20210A23). Most important environmental risk factors are aging, immobilisation, surgery, cancer, and in women also pregnancy and hormonal contracep ...
Neonatal haemophilia
... Treatment of bleeding episodes If the diagnosis of haemophilia is suspected it is important to liaise as soon as possible with a haematologist and send bloods urgently for a clotting screen (APTT, PT and fibrinogen) and factor assays. However, whilst awaiting results, the primary aim must be to trea ...
... Treatment of bleeding episodes If the diagnosis of haemophilia is suspected it is important to liaise as soon as possible with a haematologist and send bloods urgently for a clotting screen (APTT, PT and fibrinogen) and factor assays. However, whilst awaiting results, the primary aim must be to trea ...
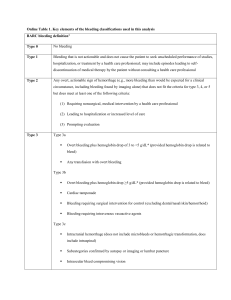
Online Table 1. Key elements of the bleeding classifications used in
... Subcategories confirmed by autopsy or imaging or lumbar puncture ...
... Subcategories confirmed by autopsy or imaging or lumbar puncture ...
factor xii deficiency an inherited bleeding
... How Factor XII Deficiency is Inherited Congenital Factor XII deficiency is an inherited coagulation protein deficiency disorder. This means that it is passed on from parent to child at the time of conception. The coagulation protein deficiency is caused by an abnormal gene. Each cell of the body con ...
... How Factor XII Deficiency is Inherited Congenital Factor XII deficiency is an inherited coagulation protein deficiency disorder. This means that it is passed on from parent to child at the time of conception. The coagulation protein deficiency is caused by an abnormal gene. Each cell of the body con ...
Mouse Models in Coagulation
... functions outside hemostasis; for example, a cleaved fragment of antithrombin III (ATIII) serves as an anti-angiogenic factor (1). Moreover, as shown remarkably by the analysis of these mouse models, many of these proteins also have a critical role in normal embryonic development (Fig. 2). Finally, ...
... functions outside hemostasis; for example, a cleaved fragment of antithrombin III (ATIII) serves as an anti-angiogenic factor (1). Moreover, as shown remarkably by the analysis of these mouse models, many of these proteins also have a critical role in normal embryonic development (Fig. 2). Finally, ...
A high-throughput sequencing test for diagnosing
... In this study, we focus on the diagnosis of rare heritable bleeding, thrombotic, and platelet disorders (BPDs). Previously, we have defined a BPD case as a patient having an abnormal platelet count, volume, morphology, or function, or with a tendency to bleed abnormally.4 The abnormal phenotypes must ...
... In this study, we focus on the diagnosis of rare heritable bleeding, thrombotic, and platelet disorders (BPDs). Previously, we have defined a BPD case as a patient having an abnormal platelet count, volume, morphology, or function, or with a tendency to bleed abnormally.4 The abnormal phenotypes must ...
Effect of a Vegetarian-like Diet on Blood Coagulation and Other
... Hemostasis: the process of arresting blood flow, as in blood coagulation Thrombosis: the presence or formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel Lectin: a protein, usually derived from plants, that is not an antibody and is not created by the immune system, but binds carbohydrate receptors on ce ...
... Hemostasis: the process of arresting blood flow, as in blood coagulation Thrombosis: the presence or formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel Lectin: a protein, usually derived from plants, that is not an antibody and is not created by the immune system, but binds carbohydrate receptors on ce ...
some in vitro effects of various concentrations of disodium
... against normal saline also accelerated the thrombin clotting time. This was true for plasma samples stored for at least 7 days. Thromboplastin activity of Al(OH)t-treated plasma. The diminished activity of Al(OH)3treated plasma samples containing excess anticoagulant was not increased by the additio ...
... against normal saline also accelerated the thrombin clotting time. This was true for plasma samples stored for at least 7 days. Thromboplastin activity of Al(OH)t-treated plasma. The diminished activity of Al(OH)3treated plasma samples containing excess anticoagulant was not increased by the additio ...
How I Treat - Blood Journal
... cross-linked by factor XIIIa, improving clot strength and preventing fibrinolysis. Fibrinogen also binds to platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors to promote platelet aggregation, further facilitating crosslinking and clot stabilization. Thus, fibrinogen is a critical component and substrate for clo ...
... cross-linked by factor XIIIa, improving clot strength and preventing fibrinolysis. Fibrinogen also binds to platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors to promote platelet aggregation, further facilitating crosslinking and clot stabilization. Thus, fibrinogen is a critical component and substrate for clo ...
2001 - Council of Europe
... donors in another 5 (14%). Prevalence and incidence of infectious diseases vary greatly among Member States, and it may be noted that in Europe a North-South gradient exists for hepatitis B and C virus. Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) for HCV is performed on each donation in 32% of Member States. In addi ...
... donors in another 5 (14%). Prevalence and incidence of infectious diseases vary greatly among Member States, and it may be noted that in Europe a North-South gradient exists for hepatitis B and C virus. Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) for HCV is performed on each donation in 32% of Member States. In addi ...
Platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to stop bleeding by clumping and clogging blood vessel injuries. Platelets have no cell nucleus: they are fragments of cytoplasm which are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow, and then enter the circulation. These unactivated platelets are biconvex discoid (lens-shaped) structures, 2–3 µm in greatest diameter. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other animals (e.g. birds, amphibians) thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells.On a stained blood smear, platelets appear as dark purple spots, about 20% the diameter of red blood cells. The smear is used to examine platelets for size, shape, qualitative number, and clumping. The ratio of platelets to red blood cells in a healthy adult is 1:10 to 1:20. The main function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: adhesion. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: activation. Third, they connect to each other through receptor bridges: aggregation. Formation of this platelet plug (primary hemostasis) is associated with activation of the coagulation cascade with resultant fibrin deposition and linking (secondary hemostasis). These processes may overlap: the spectrum is from a predominantly platelet plug, or ""white clot"" to a predominantly fibrin clot, or ""red clot"" or the more typical mixture. The final result is the clot. Some would add the subsequent clot retraction and platelet inhibition as fourth and fifth steps to the completion of the process and still others a sixth step wound repair.Low platelet concentration is thrombocytopenia and is due to either decreased production or increased destruction. Elevated platelet concentration is thrombocytosis and is either congenital, reactive (to cytokines), or due to unregulated production: one of the myeloprolerative neoplasms or certain other myeloid neoplasms. A disorder of platelet function is a thrombocytopathy.Normal platelets can respond to an abnormality on the vessel wall rather than to hemorrhage, resulting in inappropriate platelet adhesion/activation and thrombosis: the formation of a clot within an intact vessel. These arise by different mechanisms than a normal clot. Examples are: extending the fibrin clot of venous thrombosis; extending an unstable or ruptured arterial plaque, causing arterial thrombosis; and microcirculatory thrombosis. An arterial thrombus may partially obstruct blood flow, causing downstream ischemia; or completely obstruct it, causing downstream tissue death.