* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Table of Contents
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
Dodo bird verdict wikipedia , lookup
Adventure therapy wikipedia , lookup
Emotionally focused therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dyadic developmental psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
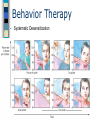
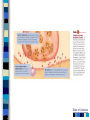
Chapter 15 Treatment of Psychological Disorders Psychoanalysis is a therapy that emphasizes a correcting habitual thinking errors . b the recovery of unconscious conflicts, . motives, and defenses c providing a supportive climate for . clients d improving interpersonal skills . Table of Contents Freud considered ____ to be the most direct way to access the patient's unconscious or the "royal road to the unconscious." a truth-serum . b hypnosis . c free association . d dreams . Table of Contents At times, individuals decide to terminate therapy at a time the therapist feels is premature and at a point when therapy is about to make significant progress. This is an example of a interpretation . b repression . c transference . d resistance Table of Contents ANSWERS B D D Table of Contents Table of Contents Trephinated Skull Table of Contents Types of Treatment Psychotherapy – Insight therapies • “talk therapy” – Behavior therapies • Changing overt behavior – Biomedical therapies • Biological functioning interventions Table of Contents Who Seeks Treatment? 15% of U.S population in a given year Most common presenting problems – Anxiety and Depression Women more than men Medical insurance Education level Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents Who Provides Treatment? Clinical psychologists Counseling psychologists Psychiatrists Clinical social workers Psychiatric nurses Counselors Table of Contents Table of Contents Psychoanalysis Developed by Sigmund Freud based on his theory of personality Table of Contents Table of Contents Insight Therapies: Psychoanalysis Sigmund Freud and followers – Goal: discover unresolved unconscious conflicts • • • • Free association Dream analysis Interpretation transference - the patient’s transfer to the analyst of emotions linked with other relationships – e.g. love you should have had for a parent focused on therapist instead. Sybil and Dr. Wilbur • resistance - blocking from consciousness of anxiety-laden material – e.g. Sybil told Dr. Wilbur it was all an act, just when they were about to get to the repressed memories Table of Contents Insight Therapies: Client Centered Therapy Carl Rogers – Goal: restructure self-concept to better correspond to reality – Therapeutic Climate • Genuineness • Unconditional positive regard • Empathy Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents Therapists who think the primary role of therapy is to assist a client in changing his or her maladaptive behavior employ a . b . c . d . behavior therapy group therapy cognitive therapy insight therapy Table of Contents Behavior therapy assumes that psychological disorders are caused by a . b . c . d . current stressful situations in one's life inconsistency between one's self-concept and reality unconscious conflicts left over from childhood past conditioning Table of Contents Systematic desensitization is a therapy designed to a . b . c . d . create a negative response to a stimulus that has elicited problematic behavior correct habitual thinking errors and maladaptive beliefs reduce phobic responses improve interpersonal skills Table of Contents ANSWERS: A D C Table of Contents Behavior Therapies B.F. Skinner and colleagues – Goal: unlearning maladaptive behavior and learning adaptive ones – Systematic Desensitization – Joseph Wolpe • Classical conditioning • Anxiety hierarchy – Aversion therapy • Alcoholism, smoking, etc. – Social skills training • Modeling • Behavioral rehearsal – Biofeedback Table of Contents Behavior Therapy Systematic Desensitization Table of Contents Systematic Desensitization Table of Contents Behavior Therapy Aversion therapy for alcoholics Table of Contents Behavior Therapy Token Economy an operant conditioning procedure that rewards desired behavior patient exchanges a token of some sort, earned for exhibiting the desired behavior, for various privileges or treats Table of Contents Behavior Therapy Exposure Therapy treat anxieties by exposing people (in imagination or reality) to the things they fear and avoid Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents Insight Therapies: Cognitive Therapy Aaron Beck – Cognitive therapy Albert Ellis – Rational-emotive therapy Goal: to change the way clients think – Detect and recognize negative thoughts – Reality testing – Kinship with behavior therapy Table of Contents Rational Emotive Therapy Developed by Albert Ellis ABC model – Activating Event – Beliefs – Consequences Identification and elimination of core irrational beliefs Table of Contents Aaron Beck’s Cognitive Therapy Problems due to negative cognitive bias that leads to distorted perceptions and interpretations of events Recognize the bias then test accuracy of these beliefs Therapist acts as model and aims for a collaborative therapeutic climate Table of Contents Cognitive Therapy Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy a popular integrated therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior) Table of Contents Table of Contents Biomedical Therapies Psychopharmacotherapy – Antianxiety - Valium, Xanax, Buspar – Antipsychotic – • Neuroleptics – all have side effects, worst is tardive dyskinesia - an incurable neurological disorder marked by involuntary writhing and tick-like movements of the mouth, tongue, face, hands, or feet • 1st generation - Chlorpromazine (Thorazine), et.al. - 1950’s - Atypical antipsychotic – reduce motor effects and other neurotransmitters • 2nd generation - Clozapine (Clozaril) – 1960’s-80’s • 3rd generation – Aripiprazole (Abilify) – 2002 • all cause tardive dyskinesia but 2nd and 3rd gen. take longer Table of Contents Biomedical Therapies – Antidepressant: • Tricyclics – Elavil, Tofranil • Mao inhibitors (MAOIs) - Nardil • Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) – Prozac, Paxil, Zoloft – Mood stabilizers • Lithium • Valproic acid Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents Therapies Inspired by Positive Psychology Martin Seligman Uses theory and research to better understand the positive, adaptive, creative, and fulfilling aspects of human existence – well-being therapy – positive psychotherapy • can be an effective treatment for depression – F 15.6 • Positive psychotherapy (PPT) contrasts with standard interventions for depression by increasing positive emotion, engagement, and meaning rather than directly targeting depressive symptoms Table of Contents Figure 15.6 Positive psychotherapy for depression Table of Contents Group and Family Therapies Family Therapy treats the family as a system views an individual’s unwanted behaviors as influenced by or directed at other family members attempts to guide family members toward positive relationships and improved communication Group Therapy support from people who know what you’re going through guidance on what you should be doing to cope good forum for opening up about problems Table of Contents Insight into childhood conflicts, motives, and feelings Self-acceptance and self-fulfillment Changing behaviors through learning Changing irrational beliefs Using free association and transference A safe nonjudgmental environment to discuss problems and unconditional positive regard Systematic Desensitization, Aversive Conditioning, and Token Economies Identification of faulty belief systems Table of Contents Current Trends and Issues in Treatment Managed care Empirically validated treatments Blending Approaches to treatment – eclectic Multicultural sensitivity Deinstitutionalization – Revolving door problem – Homelessness - Approximately 20 - 25% of the single adult homeless population suffers from some form of severe and persistent mental illness (National Resource and Training Center on Homelessness and Mental Illness, 2003) Table of Contents Table of Contents Table of Contents