* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Approaches to Psychology presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
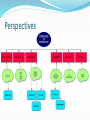
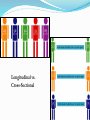
What is Psychology? The scientific study of behavior and mental processes (humans and animals) Covers what we….. • Think • Feel • Do • Largest association of Psychologists worldwide Why Study Psychology? • Application to everyday life • Gain insight into behavior (yours and others) Why Study Psychology? • Dispel myths about human behavior Goals of Psychology Describe behavior Explain behavior Predict behavior Influence behavior Nature vs. Nurture Stability vs. Change Rationality vs. Irrationality Phrenology – Examining bumps on the skull to determine intellect and character traits (19th century) Past attempts at understanding human behavior (weird or not) have led to what we know today and shaped the current Approaches to Psychology Ancient Psychology Aristotle Trephination Wilhelm Wundt • “Father of psychology” • Started 1st lab to study humans (1879) • Established Psychology as formal field of study • Introspection – self observation, report thoughts and feelings William James • “Father of MODERN Psychology” or “Father of Psychology in the U.S.” • Principles in Psychology = 1st Psychology Textbook • Psychoanalytic • Behavioral • Humanistic • Cognitive • Biological • Sociocultural Perspectives PSYCHOANALYTIC/ PSYCHODYNAMIC • Key ideas • childhood experiences • unconscious forces • Sigmund Freud (1856 – 1939) • Unconscious motivations are responsible for human behavior • Techniques: • Free association • Psychoanalysis • Dream analysis BEHAVIORAL • Key ideas • Observable Behavior • Conditioning/Learning • Prior experience • John Watson (1878 – 1958) • Behavior the result of conditioning – “We are what we learn to be” • B.F. Skinner (1904 – 1990) • Reinforcement HUMANISTIC • Key ideas • Self-directed • Uniqueness • Potential to develop EVOLUTIONARY Key Ideas: Survival of the fittest Inheritable traits Success Main theorist: Charles Darwin COGNITIVE • Key ideas • How we ….. Process, Store, Retrieve information • Thought patterns • Problem solving • Behavior results from memories, expectations BIOLOGICAL • A.k.a. Behavioral neuroscience • Key ideas • How the brain, nervous system, hormones, genetics influence behavior SOCIOCULTURAL Key ideas • Cultural influence on behavior • Gender • Socioeconomic status Eclecticism • By combining information from all of the approaches, psychologists stand a better chance of describing, explaining, predicting, and controlling behavior. Psychologist • Observe, analyze, evaluate behavior • Doctorate degree Psychiatrist • Medical degree + training in psychiatric medicine Clinical Psychologist • diagnoses and treats people with emotional disturbances Counseling Psychologist • help people deal with problems of everyday life Developmental Psychologist • Study changes that occur throughout life Educational Psychologist • helps students learn Industrial/Organizational Psychologist • employed by businesses to boost production, improve working conditions, make the workplace a more satisfying environment Research v. Applied Psychology Research Psychologists – study origins, causes, results of behavior Applied Psychologists – make direct use of the findings of research psychologist; deal directly with clients Naturalistic Observation • Observe subjects in a natural setting without interfering • Natural behavior Case Study • Intensive investigation of one or more participants • long-term observations, diaries, tests, interviews Survey • Interviews, questionnaires, or both • asking many individuals a fixed set of questions Longitudinal Study • Data is collected over a number of years • Development • time-consuming Cross-sectional Study • Different age groups – same time – compare Longitudinal vs. Cross-Sectional Double-Blind Experiment • Neither participants nor experiment knows which received medication • keeps researcher unbiased Placebo effect • change in illness/physical state from knowledge and perception of treatment • believing it will have an effect • fake medication