* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3 Final Exam Review Pre Civil War through
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
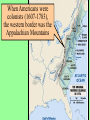
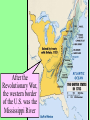
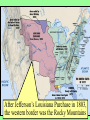
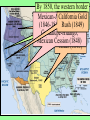
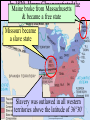
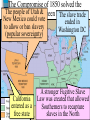
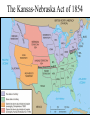
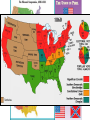
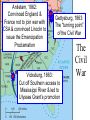
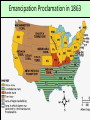
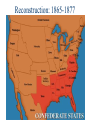
US History Review The Late Antebellum Era (1840-1860) When Americans were colonists (1607-1783), the western border was the Appalachian Mountains After the Revolutionary War, the western border of the U.S. was the Mississippi River After Jefferson’s Louisiana Purchase in 1803, the western border was the Rocky Mountains By 1850, the western border was the Pacific Ocean Mexican-American Annexation California War Gold of from Oregon to California (1846-1848), Oregon Rush Treaty (1849) (1846) of Guadalupe-Hidalgo, Annexation of Mexican Cession (1848) Texas (1845) InMaine 1820,broke Henry Clay negotiated the from Massachusetts Missouri & became Compromise a free state Missouri became a slave state Slavery was outlawed in all western territories above the latitude of 36°30' The Compromise of 1850 solved the The peopledispute of Utahbetween & sectional North & South The slave trade New Mexico could vote to allow or ban slavery (popular sovereignty) California entered as a free state ended in Washington DC A stronger Fugitive Slave Law was created that allowed Southerners to recapture slaves in the North Abolitionists The Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 The Civil War & Reconstruction (1861-1877) The Confederate States of America Advantages of the Union & Confederacy Antietam, 1862: Convinced England & France not to join war with CSA & convinced Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation Gettysburg, 1863: The “turning point” of the Civil War Vicksburg, 1863: Cut off Southern access to Mississippi River & led to Ulysses Grant’s promotion The Civil War Emancipation Proclamation in 1863 Reconstruction: 1865-1877 ■ Presidential Reconstruction (A Johnson) –States could come back into the USA once they ratified the 13th Amendment –Southerners created black codes to keep African-Americans inferior ■ Congressional Reconstruction (led by the “Radical Republicans”) –The South was placed under military rule & divided into 5 zones –Southern states were forced to ratify the 14th & 15th Amendments Reconstruction Legislation ■ From 1865 to 1877, blacks were protected & given rights as citizens –13th Amendment ended slavery –14th Amendment made it illegal to discriminate against people due to race, gender, religion –15th Amendment gave all black men the right to vote –Freedman’s Bureau created to provide food, 40 acres & a mule, & schools for African-Americans Radical Reconstruction (1867-1877) Created 5 military districts to enforce Reconstruction But, Radical Reconstruction was not adequate to enforce equality in the South Black codes were common in many parts of the South A secret society called the Ku Klux Klan was created to keep blacks inferior & return “Redeemer Democrats” to power ■ Andrew Johnson’s Impeachment: –President Johnson interfered with the “Radical Reconstruction” plan & was the 1st president to be impeached –But he was not removed from office ■ The end of Reconstruction: –The “Second Corrupt Bargain” (the “Compromise of 1877”) –President Hayes removed federal troops & ended military zones –“Jim Crow” era began (1877-1954) –Legal segregation in the South Jim Crow Era (1877 to 1954) ■ Jim Crow laws keep blacks from voting –Literacy tests—voters have to read –Poll taxes—voters must pay a tax –Grandfather clauses—allowed whites to avoid literacy test & poll taxes ■ In Plessy v Ferguson (1896), the Supreme Court said segregation was OK (“separate but equal”) “Jim Crow” South from 1877 to 1954