* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Start of the Civil War
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Fort Pulaski wikipedia , lookup
Lancashire Cotton Famine wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Ex parte Merryman wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Henry wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Habeas Corpus Suspension Act (1863) wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
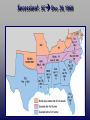
The Civil War (1861-1865) Secession!: SC Dec. 20, 1860 Fort Sumter: April 12, 1861 • Confederate officials began seizing federal-mint branches, arsenals, and military posts. • Fort Sumter was a Federal outpost in Charleston, SC. Fort Sumter: April 12, 1861 • Confederate forces asked for its surrender. • Lincoln refused and sent ships with supplies. • Confederate cannons began firing on April 12, 1861. • Fort Sumter fell 34 hours later. • The Civil War began. Rating the North & South Slave/Free States Population, 1861 Railroad Lines, 1860 Resources: North & South Men Present for Duty in the Civil War The Union & Confederacy in 1861 The Leaders of the Confederacy Pres. Jefferson Davis VP Alexander Stevens Opposing Sides Yankees (North) Pros and Cons Rebels (South) Pros and Cons Overview of Northern Advantages (pros) • Larger population – North 22 million – South Only 9 million • • • • • More ships-naval wars Larger, more efficient railroad system Lincoln - Very intelligent and dedicated More industry - 81% of nation’s factories Better banking system to raise $ for the war – 75% of nation’s wealth Overview of Northern Advantages • Wealth produced: – Factory production – Iron/Coal production – Wheat/Corn production Overview of Northern Disadvantages (cons) • Fought on Southern lands • Divided support for the war • Many believed the South had good chance of winning Overview of Southern Advantages • Fighting a defensive war – Local support of all men – familiarity with terrain • Motivation: seeking independence, unified support • Short communication lines/ friendly population • Experienced officer corps- (Lee, Jackson, Pickett) • Cotton - necessary for textile factories of England and France • Slave Labor in the early part of the war Overview of Southern Disadvantages • Smaller population • Few factories to manufacture weapons and supplies • Poor transportation system • Weak federal government = not strong enough to control Southern states – Jefferson Davis did not have complete power like Lincoln Legal Tender Act • • • • • Passed in Feb 1862 by US Congress Created a national currency Introduced paper money (greenbacks) More money available in emergency Decreased inflation, which helped money keep value. • The South tried to issue paper money, but with no revenue, it was worthless. Democratic Division • Lincoln had to deal with abolitionists, who wanted to end slavery but his main goal was to preserve the Union. Also, he had to contend with Democrats. • War Democrats-strongly supported war to restore the Union/ pro-slavery • Copperheads (Peace Democrats)- opposed war, wanted to use negotiation, anti-slavery, viewed as traitors (snakes) • Two main disagreements- conscription and habeas corpus. Conscription in the North • Forcing people through a military draft when needed. (north) • Republicans (for it) and Northern Democrats (opposed it) • Democratic states rioted over issue. Habeas Corpus (North) • The writs of h.c.-A person’s right not to be imprisoned unless charged with a crime and given trial, otherwise they are freed. • Suspended under Lincoln during war. • Applies to Who? Anyone supporting rebels or resists military draft • Penalty: imprisonment indefinitely Industry • South- pressure Britain and France to aid them due to their dependence on cotton, which was needed for textile industry. • North- didn’t want Europe to get involved • Trent Affair- Confederate diplomats are captured and imprisoned by Union warship, while attempting to meet with European officials to seek allied help. Technology/ Tactics • 1st modern war • –Rifled muskets/cone shaped bullets. This allowed killing at a longer distance with far more accuracy. • –Use of the railroad. The ability to go troops quickly (especially cannon or infantry–forces not usually associated with quick movement) • –Communication. Before, you relied on riders or runners, now they had telegraph wires • – Naval Warfare. Introduced to ironclad ships, the submarine • --Use of trenches as part of a mobile battlefield. • -- Attrition. Wear down on side through exhaustion and cutting off resources Anaconda Plan • Northern Strategy v. Southern Strategy Overview North’s Civil War Strategy: “Anaconda” Plan Goal: surround the Confederacy and squeeze them into submission The Anaconda Plan • Capture Richmond and force surrender • Expel Confederates from border states • Control of the Mississippi River to Stop the transport of: – – – – – – soldiers Weapons Ammunition Clothes Food other supplies needed • Blockade southern ports to stop – cotton shipments – supplies from foreign nations Southern Strategy • Goal: to be recognized as an independent nation in order to preserve their way of life • Defend its homeland, holding onto as much territory as possible until the North got tired of fighting • Capture Washington, D.C. • Control border states • Gain England's support • Expel Union troops from South