* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Harpers Ferry wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Northern Virginia Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Maryland Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
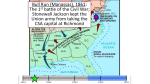
The Civil War: 1861 - 1865 "...WE HERE HIGHLY RESOLVE THAT THESE DEAD SHALL NOT HAVE DIED IN VAIN; THAT THIS NATION, UNDER GOD, SHALL HAVE A NEW BIRTH OF FREEDOM; AND THAT GOVERNMENT OF THE PEOPLE, BY THE PEOPLE, FOR THE PEOPLE, SHALL NOT PERISH FROM THE EARTH." -ABRAHAM LINCOLNTHE GETTYSBURG ADDRESS Confederate States of America Model constitution after US Single six-year term, line item veto power for Pres. No power to levy tariff No funds for internal improvements Prohibit foreign slave trade JD = President Limited c. gov. States more sovereign than “fed” gov. Secession of parts of states (GA) Money issues $1 bil. in CSA $, 10% tax (in kind), impressment (private property), nat’lization of RR & industrial development “This country will be drenched in blood…The people of the North… are not going to let this country be destroyed without a mighty effort to save it…Besides, where are your men and appliances of war to contend against them?...You are rushing into war with one of the most powerful, ingeniously mechanical and determined people on earth- right at your doors…Only in spirit and determination are you prepared for war. In all else you are totally unprepared.” -William Tecumseh Sherman Confederate seizure of Union Federal Installations in South For US- defend or give over to CSA? Fort Pickens- Pensacola, FL Fort Sumter- Charleston, SC April 12th, 1861: WAR BEGINS! Use of Executive Power Lincoln increase power as chief exec. & CinC- no authorization from Congress 1. call for 75k troops- put down “insurrection” in CSA 2. OK to spend US $$ for war 3. suspend writ of habeas corpus Arrest w/ no charge or trial OK Copperheads MD situation • Arrest of mayor, police chief, city council - Baltimore • Taney • Frank Key Howard- 14 months at the American Bastille The War is on. . . Post- Fort Sumter- 4 more states into CSA b/c Lincoln willing to use troops in crisis Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, Tennessee Four slave states stayed in the Union: Maryland, Delaware, Kentucky, Missouri • 1863- WV Capital of CSA from Montgomery Richmond The Union vs. The Confederacy Union Advantages were their resources: had more People Factories Food production Extensive rail system 3- Point Strategy: Navy blockade of Southern ports (Anaconda Plan) Conquer the MS River/Split CSA in two Capture Richmond, VA (capital) Confederacy Advantages were: Highly trained/effective generals motivated soldiers resourcefulness/fighting in own territory Strategy: Defend the CSA Attack Union when opportunity arises CSA v. USA: MILITARY CSA USA Defense = offense Must conquer CSA Size of Europe Short distance for troops, supplies Coast difficult to blockade Experienced military leaders High morale Long distance war High pop. useful in war of attrition + Immigrants, emancipation US Navy CSA v. USA: ECONOMY CSA USA AG based Cash crops Banking King Cotton 85% of US factories Confederate $$ 70% of RR inflation Control of capital 65% of farmland Logistic savvy CSA v. USA: POLITICS CSA USA Struggle for Preservation of Union independence States’ rights issues liability To win- need strong c. gov., public support Suspension of civil rights Victory? Turn people vs. Union/Abe/War Strong c. gov. + public support Suspension of civil rights Border States Why not DE, MD, MO, KY? Union sentiment, federal policy MD: pro-secessionist attack Union troops, threats to destroy RR to DC, PA martial law, suspension of HC state under federal control MO- US troops block pro-South forces Guerrilla forces throughout war KY- vote to remain neutral CSA violate federal troops in Loss of border states CSA population up 50%, resources, transportation/communication networks No emancipation @ start of war to appease Unionists in border states "I hope to have God on my side, but I must have Kentucky." First Battle of Manassas The Battle of Bull Run July 21, 1861 Back & forth between USA & CSA North- Brig. General McDowell South led by Brig. General P.G.T. Beauregard, General Thomas Jackson “There stands Jackson like a stone wall!” Col. Francis Bartow- 1st Commander to die in the Civil War CSA win = war of attrition, rebs as “invincible” Improved weapons (minie ball, grenade, submarine), trenches Strategy of the Union Anaconda Plan McClellan- Richmond MS- Grant, Farragut (sea) Blockade March 8, 1862- Monitor v. Virginia (Merimack)/Hampton Roads Effect? Peninsula Campaign Gen. George McClellan v. Gen. Robert E. Lee Western Theater U.S. Grant- TN Shiloh Antietam/ Sharpsburg September 17, 1862 War for Capitals: Antietam Sept., 1862: CSA/ANV DC Victory in USA = support/recognition from GB failure Lee/ANV cross Potomac MD Plans exposed- McClellan takes advantage Sept. 17th: USA v. CSA - Antietam Creek. Bloodiest single-day battle in U.S. history 22k+ wounded/dead. Lee back to VA = Union victory. Union Gen. McClellan not pursue retreating CSA Lincoln removal from command “bad case of the slows” Emancipation Proclamation Abe use as opportunity to change purpose of war. Draft of EP prior to battle Use to weaken the CSA. War powers = seizure of enemy resources/contraband. Slaves = resource/contraband ONLY in CSA EP- Sep. 22, 1862 effective Jan. 1, 1863. Before EP= war on economics of slavery, states v. federal rights, to preserve the Union (or Southern independence) After EP = war also about moral issue of slavery. Emancipation Emancipation Why not earlier? Need support of border states Constitutional protection of slavery Racial prejudice of N Election of 1864 EP = Freedman into War 200k serve in Union army 37k dead Army of Freedom Segregated Mass. 54th Regiment Foreign Affairs Desire for foreign aid GB & King Cotton Breakdown of US democratic experiment (pol. & econ. effects) Trent Affair 1861- James Mason & John Slidell on the British Trent Captured by US, prisoners of war threat of war b/t GB/USA Lincoln apology, release No recognition Alabama CSA buy GB warships, raiders (‘bama- 60+ vessels captured before sunk by USA) Laird ram purchase blocked by US (threat of war w/ GB if sell) King Cotton fails Cotton from India, Egypt Other materials- wool, linen No CSA recognition by GB/France Lee’s loss @ Antietam Emancipation Proclamation Benefit of trade w/ USA Turning Points Vicksburg Spring, 1863- USA control New Orleans, most MS river/valley Grant attempt to take Vicksburg Fortified, on hill overlooking MS River USA destroy rail lines, distract CSA troops near Jackson While Union infantry to Vicksburg. April 30 = start of siege --> Confederate surrender on July 4 An Invasion into the North Lee intent to invade North = Gettysburg Victory force Union to call for peace, foreign intervention Go through MD, into PA N support for war minimal. soldiers deserting Attempts to undermine Lincoln, war effort July 1st – 3rd, 1863 CSA retreat No more offensive, no more invasion of N Gettysburg Address November 1863: Ceremony to dedicate cemetery @ Gettysburg People to see U.S. in a new way Was not a collection of individual states, but a UNIFIED NATION The War Turns War of Attrition Grant OK w/ war style- attrition Grant E to VA- commander of all USA armies Victory through… Use of population of resource Destruction of CSA supply lines Wear down CSA army Vs. Lee CSA army #s low, retreat to defense of Richmond Total war Sherman’s March to the Sea 100k men- Chattanooga Atlanta (Sept., 64- election year), Savannah (Dec.), Columbia (Feb., 65) Election of ‘64 Dems- McClellan Call for peace! Appeal to war-weary Repub = Unionist Party Lincoln + Johnson Appeal to “War Democrats” Gettysburg, Vicksburg Republican win, reelection 212 EC to 21 EC BUT… McClellan 45% of pop. vote War Ends Successful blockade + Sherman’s march + starvation in S (winter, ’64-’65) Lee lines collapse @ Petersburg April 3rd, 1865: Union take Richmond surrender @ Appomattox Courthouse Lee attempt to retreat into mtns- cut off, forced surrender Abe want restoration of Union vs. Davis demand for continued independence- CSA gov. negotiation for peace fail Surrender at Appomattox Courthouse April 9th - Lee & Grant meet, arrange surrender generous terms of surrender Grant took over Lee’s soldiers, sent them home w/ possessions and few days worth of rations. By May, all Confederate resistance collapsed. The Civil War ends w/ Union preserved Death toll almost as many deaths as all other US wars combined Union- 360,000 CSA- 260,000 TOTAL: 620,000 Lincoln Assassination March, 1865: Booth + friends plan kidnapping Lincoln taken to Richmond, VA exchange for Confederate prisoners Lincoln did not arrive at time/place, so plan failed April, 1865: Plot to save Confederacy Kill Lincoln, VP Andrew Johnson, & Sec. of State William Seward April 14th, 1865: Lincoln’s to Ford’s Theater in DC to see Our American Cousin 3rd act, “unknown” shooter into box Lincoln shot from behind (head) Sic Semper Tyrannus= Thus always to tyrants! Virginia, Caesar Lincoln paralyzed, died April 15th, 1865 Booth caught 12 days later in in Virginia Other two parts of plan failed