* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the discriminatory acts of one race or ethnic group against another
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
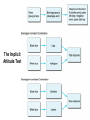
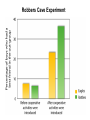
Racial / Ethnic Prejudice and Discrimination I. Stereotypes, Prejudice, and Discrimination A. Stereotype: a generalized belief about a group of people in which identical characteristics are assigned to virtually all members of the group, regardless of actual variation among the members. B. Prejudice: an attitude or feeling, favorable or unfavorable, toward a person or group of people, prior to, or not based on, actual experience. C. Discrimination: an unjustified negative or harmful behavior toward a member or members of a group simply because of their membership in that group. II. Racism: an individual’s or group’s prejudicial attitudes and discriminatory behaviors toward people of a given race or ethnicity. A. Individual Racism: the racist acts of one person based on conscious or unconscious prejudice. B. Institutional Racism: when economic, educational, political, social, and corporate institutions favor one race or ethnicity over another. C. Cultural Racism: the discriminatory acts of one race or ethnic group against another race or ethnic group, at times attempting to change or eliminate the other group. D. Racial Discrimination… Does it still exist? E. Are most people individual racists? 1) Subtle Racism 2) Automatic Racism The Implicit Attitude Test III. Key Motivational & Cognitive Influences in Prejudice and Discrimination A. Scapegoating: the idea that you use a particular person or group of people (usually people not in a position to effectively retaliate) to act out aggression upon in order to vent frustration. B. Evolutionary Survival Instinct: difference is a sign of danger. C. The Ultimate Attribution Error: the tendency to make dispositional attributions from one individual’s characteristics or behavior to an entire group of people. IV. Prejudice and Discrimination: Remedies A. Contact Hypothesis: the idea that prejudice and discrimination will decline as we have more contact with people who we would have discriminated against. B. Mutual Interdependence: the need to depend on each other to accomplish a goal that is important to each group. Both contact and mutual interdependence combined is most effective in reducing Prejudice and Discrimination. Robbers Cave Experiment