* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
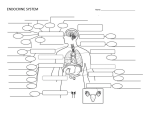
The Endocrine System How our hormones function The Endocrine System Clip What is the Endocrine System? Series of cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids (blood). Hormone= a chemical secreted by endocrine glands which has a specific effect on another cell or organ. Where are the major endocrine glands located? • Added info – Gland= organ that is made up of epithelial tissue – Secrete hormones. • • • • • • What do hormones control? Reproduction Growth and development Maintain homeostasis Regulation of metabolism Increasing bodies defenses Gets “stuff” through cell membranes. How do hormones work? Hormones are produced by specialized cells in glands. Glands secrete hormones into extra-cellular fluids Blood transfers hormones to target sites Hormones cause changes in target cells What organic compounds are hormones made of? Amino acid-based hormones Steroids – made from cholesterol; sex hormones, and adrenal cortex Prostaglandins – local hormones made from lipids What are the two types of hormones? Fig 9.1 • Steroid Hormones – Soluble in fat. Penetrate cell membrane. – Reach nucleus • Nonsteroid Hormones – Not soluble in fat. Bind to cell membrane. – Cascade of chemical reactions. Steroid Hormone Adrenalin The non Steroid Hormone How are Hormone Secretions Controlled? Negative Feedback System Neg. Sys. Gland A secretes causing Gland B to secrete. Gland B’s secretions inhibit A. Like a thermostat. Nerve Control Controlled by the brain. Complicated. There are Positive feedback systemsbut they are limited. What can go wrong if there is a loss of hormonal control? • Dwarfism (Hypopitutiary dwarfism) – GH= Growth hormone – When inadequate amounts are secreted. – Short, underdeveloped, lack full adult sexual features. – Treatment: Hormone therapy if diagnosed early Dwarfism Movies Gigantism can also be an issue. • Too much growth hormone. • 8ft + • Usually caused by a tumor that has developed in the pituitary gland causing too much GH to be secreted. • Life expectancy is not full due to strain on the heart. The Pituitary Gland Location: Between the eyes and ears. Hangs by the hypothalamus stalk. Has two functional lobes Anterior pituitary – glandular tissue Posterior pituitary – nervous tissue 6 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Growth Hormone (GH)- Stimulates Mitosis Prolactin- Milk Production After Birth of Baby Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)- Plays role in Metabolism Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) And Luteinizing hormone (LH)- Releases egg from follicle & regulates testosterone Pituitary And Hormones Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)- Stimulates follicles to develop in the ovaries & sperm to develop in the testes. The 2 Hormones of the Posterior Pituitary Oxytocin- Contracts uterus during labor & stimulates milk ejection. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)- Inhibits urine production, can increase blood pressure through vasoconstriction/water retention. Thyroid Gland Butterfly shape at the base of the throat Produces two hormones Thyroid hormones (T4 & T3) regulate the metabolism of carbs, lipids, & proteins. Calcitonin decrease Ca+ in the blood (more for your bones). Thyroid Gland Rotation What can go wrong with the Thyroid? A goiter. A lack of Iodine in the diet (3rd world countries) or too much TSH (Thyroid Stimulating hormone) Thyroid Gland Tumor Parathyroid Glands Parathyroid Gland Rotation On each of the 4 corners of the thyroid. Stimulate osteoclasts to remove calcium from bone Stimulate the kidneys and intestine to absorb more calcium Raise calcium levels in the blood Adrenal Glands Two glands Cortex – outer glandular region Medulla – inner neural tissue region Sit on top of the kidneys Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex Glucocorticoids (including cortisone and cortisol) Increases the use of fat, proteins (A.A) and sugar when body needs energy Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) Regulate electrolyte balance Target organ is the kidney Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex Sex hormones Produced in the inner layer of the adrenal cortex Androgens (male) and some estrogen (female) Hormones of the Adrenal Medulla Produces two similar hormones that prepare the body to deal with short-term stress Epinephrine Norepinephrine Pancreatic Islets The pancreas, Insulin, Glucose, & Diabetes The islets of the pancreas produce hormones Insulin – allows glucose to cross plasma membranes into cells from beta cells Glucagon – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells These hormones are antagonists that maintain blood sugar homeostasis. Pineal Gland Found on the third ventricle of the brain Secretes melatonin Helps establish the body’s wake and sleep cycles Thymus Located posterior to sternum Largest in infants and children Produces thymosin Matures some types of white blood cells Important in developing the immune system Hormones of the Ovaries Estrogens Stimulates the development of secondary female characteristics Matures female reproductive organs Also produced by the placenta. Estrogen, continued Helps prepare the uterus to receive a fertilized egg Helps maintain pregnancy Prepares the breasts to produce milk Progesterone Produced by the corpus luteum Acts with estrogen to bring about the menstrual cycle Helps in the implantation of an embryo in the uterus Hormones of the Testes Interstitial cells of testes are hormone-producing Produce several androgens Testosterone is the most important of them. Testosterone Responsible for adult male secondary sex characteristics Promotes growth and maturation of male reproductive system Required for sperm cell production Other Hormone Producing Tissues and Organs Parts of the small intestine Parts of the stomach Kidneys Heart Many other areas have scattered endocrine cells Placenta Development Aspects of the Endocrine System Menopause Growth hormone production declines with age Many endocrine glands decrease output with age