* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLS
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
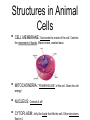
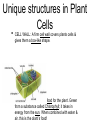
CELLS By Amy Lamarre- DWE Objective • Today I can compare parts of plants & animals that are needed for growth & survival Essential Questions 1. What are plant structures? How do they help plants in growth and survival? 2. What are animal structures? How do they help animals in growth and survival? 3. What are some of the similarities in plants and animals? How are they different? SET • Picture in your mind an animal. Think about all the internal body parts that work together to help that animal survive. • On your whiteboard, make a list of all the parts (large & small) that help this animal survive. Organisms • Any living thing is called an organism. • In plants and animals, we call the parts of microscopic organisms structures. • The different parts of each structure each have a function or “a job”. Cells • Cells are the smallest living part in animals and plants. • Plant and animal cells are different, although many of the structures are the same. • Living things such as humans, trees, dogs and lions are ALL made up of TRILLIONS of cells! Animal Cells • Mammals, including humans are made up of various types of cells. • Most animals & all humans have bone cells, nerve cells, muscle cells and blood cells, to name a few. • Each type of cell has a different job to keep the body functioning properly. Structures in Animal Cells • CELL MEMBRANE: Surrounds the inside of the cell. Controls the movement of liquids. Water enters, wastes leave. • MITOCHONDRIA: “POWERHOUSE” of the cell. Gives the cell energy! • • NUCLEUS: Controls it all! CYTOPLASM: Jelly-like liquid that fills the cell. Other structures Plant Cells • Plants are living organisms and have cells similar to an animal cell. • Instead of having cells like those that support our blood & bones, plants have cells that support its leaves and roots. • A plant’s leaf cells make food for the plant. • A plant cell has all the parts of an animal cell, but also has a Cell Wall & Chloroplasts. Unique structures in Plant Cells • • CELL WALL: A firm cell wall covers plants cells & gives them a box-like shape. CHLOROPLASTS: Make food for the plant. Green from a substance called Chlorophyll; it takes in energy from the sun. When combined with water & CLOSURE • Think in your mind, the two structures that are unique to a plant cell. Turn and tell your shoulder partner those two parts. • On the back of your notes, write a 20 cent summary (20 words) about why cells are important for the survival of mammals and plants.