* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Matter and Its Changes
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
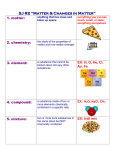
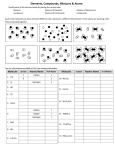
Riddle It can be anything, and it makes up everything. But it always takes up space and has mass. What it is? Matter and Its Changes Chapter 2.1 Chemistry 1.1 Chemistry: Definition The study of properties of matter and how it changes What is Matter? Anything that: Has Mass Takes up Space (volume) Building Blocks of Matter Elements: Cannot be broken down into any other substance by chemical or physical means All matter around you is composed of one element or a combination of elements Building Blocks of Matter - 2 Molecule: 2 or more atoms chemically bonded together, making a new substance Compound: A molecule made of 2 or more elements, making a new substance Building Blocks of Matter - 3 Mixture: 2 or more substances mixed by not bonded to make a new substance Solution: a well mixed mixture in liquid form (salt water) Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Homo – means same Hetero – means different Homogeneous mixture is the same everywhere Can’t see individual pieces, can’t filter Heterogeneous mixture is not the same everywhere Different in different places Can see the pieces Can filter usually Mixing Liquids Miscible two liquids that dissolve in each other. They mix to form a solution Immiscible Two liquids that don’t mix and stay mixed. They may make a suspension, but they don’t make a solution Changes in Matter - 1 Physical Change: change in form or appearance that does not change the actual substance (ice to water to steam) Changes in Matter - 2 Chemical Change: substances mix to form new substances with different properties Observing Chemical Reactions Key Characteristic: production of new materials that are chemically different from the starting materials Gas released Temperature change New solid material Smell etc Chemical Reactions on a Small Scale ONE (1) particle of an element is an ATOM Molecule – 2 or more atoms combined Chemical Reactions on a Small Scale Chemical BONDS are the ‘glue’ that holds atoms together Chemical REACTIONS occur when chemical bonds are formed or broken. Section 1.1 Review Questions 1. How are element, Element cannot be compound, mixture broken down. different? Compound is two or more elements combined chemically. Mixture is 2 or more items that can be physically separated Section 1.1 Review Questions 2. What forms of evidence show a chemical reaction has take place? 3. What happens to chemical bonds in a chemical reaction? New substances are formed, can be seen by color, precipitation, gas released, temperature changes, changes in properties. Bonds are broken or new bonds may form Section 1.1 Review Questions 4. What is difference between atom and molecule? 5. Classify changes: for Ice cream, sugar, gasoline, mirror, milk Atom is smallest particle of an element. Molecule is combination of 2 or more atoms Ice cream melting is physical. Sugar dissolving is physical Gasoline burning is chemical mirror fogging is physical milk souring is chemical