* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
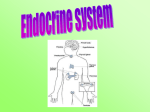
The Endocrine System Functions: Controls the conditions in your body by making and sending chemicals from one part of the body to another This is called_____________ Most responses are controlled by the nervous system Hormones: Chemicals that are made in one organ and travel through the blood to a second organ Second organ (target organ) responds to the chemical Different hormones perform different jobs Glands Main structures of the endocrine system Main organs Produce hormones and release them into the circulatory system Pituitary Gland “Director” of the system Produces hormones that control: Growth Sexual development Absorption of water into the blood by the kidneys Hypothalamus Attached to the pituitary gland Primary connection between nervous and endocrine systems Secretions of the pituitary gland are controlled here Produces releasing hormones Pineal Gland Sensitive to different levels of light Essential to rhythms such as sleep, body temperature, reproduction and aging Thyroid Gland Releases hormones for growth and metabolism Stores the thyroid hormone Produces calcitonin Helps regulate calcium in the body Thymus Helps body fight disease by controlling the production of white blood cells (t-cells) Adrenal Glands Secrete 30 different hormones that regulate carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism and water and salt levels in your body Fights allergies and infections Produces adrenaline Makes your heart beat faster Relaxes the muscles in the lungs Pancreas Secretes 2 hormones Insulin Glucagon Regulates the level of glucose in your body Diabetes Type I and Type II Ovaries and Testes Secrete hormones that control sexual development Male-Testes Female-Ovaries Other Organs Kidneys Secrete hormone that regulates production of red blood cells Heart Produces two hormones that help regulate blood pressure Feedback Mechanisms Used to maintain homeostasis Negative Feedback Final effect of the response is to turn off the response Positive Feedback Increases response due to extreme circumstances Hormone Balance Action One hormone is balanced by the action of another Hormone imbalance can cause serious disease Diabetes Hypothyroidism hyperthyroidism