* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
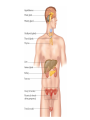
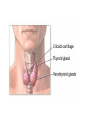
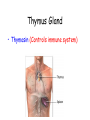
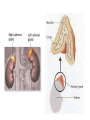
Endocrine System Glands & Hormones Hormone A chemical messenger that is produced at one site and carried by the blood to its site of action (target cells) Pituitary Gland 1. ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) Stimulates adrenal glands to make Cortisol and aldosterone 2. ADH (Antidiuretic hormone) Causes kidneys to reabsorb more water preventing dehydration 3. GH (Growth hormone) (Causes bone and muscle growth) 4. TSH (Thyroid stimulating hormone) (Stimulates thyroid gland to make T3 and T4) Pituitary Gland 5. LH (Luitenizing hormone) (Stimulates estrogen & progesterone secretion from ovaries & testosterone secretion from testes) 6. FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) (Egg & sperm production) 7. Oxytocin (Causes uterine contractions) 8. Prolactin (milk production) Pineal Gland • Melatonin (Initiates sleep) Thyroid Gland T3 (Triiodothyronine) (Controls metabolism) T4 (Thyroxin) (Controls metabolism) • Calcitonin (Builds up bone to lower blood calcium) Parathyroid Gland • PTH (Parathyroid hormone) (Breaks down bone to raise blood calcium) Thymus Gland • Thymosin (Controls immune system) Pancreas • Insulin (Allows glucose to enter cells; LOWERS blood glucose) • Glucagon (Stimulates liver to make glucose; RAISES blood glucose) Adrenal Glands Medulla a. Epinephrine (adrenaline) (Increases: blood glucose, heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, & dilates bronchioles) b. Nor-epinephrine (nor-adrenaline) (Same as Epinephrine) Adrenal Glands Cortex a. Cortisol (Stress released to increase blood glucose) b. Aldosterone (Controls salt & water balance) c. Androgens (small amounts of estrogen and testosterone) Ovaries • 1. Estrogen (Creates female secondary sex characteristics) • 2. Progesterone (Thickens the uterus lining each month) Testes • 1. Testosterone (Creates male secondary sex characteristics) Kidneys • Renin and Angiotensinogen which control blood volume Heart • ANP (Atrial Naturetic Polypeptide) which causes Na ions to be excreted in the kidney (Lose water & ultimately blood pressure) Negative Feedback