* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy and Energy Resources
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
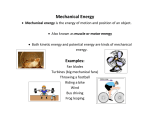
Energy and Energy Resources Carin Miranda Smyrna Middle School Fall 2009 What is Energy? • Energy is the ability to do work. • Energy is expressed in joules (J). Kinetic Energy • Kinetic Energy is the energy of motion. • Kinetic Energy = mv2 / 2 Potential Energy • The Energy an object has based on shape or position. • Elastic potential energy – When you change the shape of something • Gravitational potential energy – The higher something is off the ground the higher its potential energy. The more it weighs the higher its potential energy as well. Depends on height and weight. • Chemical potential energy – The food you eat is stored as chemical potential energy Mechanical Energy • Is the total amount of energy in a system. • Mechanical energy= potential energy + kinetic energy • As kinetic energy goes up potential goes down and vice verse. Other Forms of Energy • • • • • • Thermal Chemical Electrical Sound Light Nuclear Thermal Energy • Heat • Higher the temperature the faster the molecules move • The more you have of a substance the more thermal energy you have. Chemical Energy • Food you eat • Batteries • Anytime you have something breaking down and it creates a new object. Electrical Energy • Moving electrons • Anything you plug in. • Batteries start as chemical energy but it is converted into electrical energy. Sound energy • Caused by an objects vibrations • Anything you hear Light Energy • Vibrations of electrically charged particles • Anything you see. • Waves that you can’t see – Radio, Gamma, ultraviolet, microwaves Nuclear Energy • When two atoms fuse together(fusion) or split apart (fission) • Fusion happens in the sun • Fission happens when uranium is split to produce electrical energy Energy Conversions • A change from one form of energy to another. • Any form of energy can be converted into any other form of energy. Energy Conversions in Plants • The nuclear energy of the sun produces light and thermal energy. • The light energy from the sun is converted by plants into chemical energy which is stored in the foods we eat. Conservation of Energy • Roller Coaster- Highest potential energy is at the top of the biggest hill. Highest kinetic energy is at the bottom of the biggest hill. Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy can never be created nor destroyed. • It can only be transferred or converted. • In every energy conversion some thermal energy is given off due to friction. • This means that there is no such thing as a perpetual motion machine. Energy Efficient? • The amount of energy available before a conversion compared to the amount of useful energy after a conversion. Energy Resources • A natural resource that can be converted into other forms of energy • Nonrenewable – Cannot be replaced or are replaced at a slower rate than we are using it. • Renewable – Can easily be replaced. Nonrenewable Resources Fossil Fuels • Includes coal, natural gas, petroleum. • Most coal is used to generate electrical energy. Nuclear Energy Uranium 1 uranium= 1 metric ton of coal. Renewable • • • • • Solar Water (Hydroelectric) Wind Geothermal (hot water under ground) Biomass (trash) Advantages vs. Disadvantages Know all the advantages and Disadvantages of the Energy Resources on Page 368