* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Conversions and Conservation
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
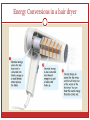
Energy Conversions and Conservation CHAPTER 9 SECTIONS 2-3 Types of Heat Transfer Convection – transfer of thermal energy by the movement of a liquid or gas Conduction - Particles from a warmer object transfer by colliding with particles from the cooler object. Radiation - Thermal energy transferred through electromagnetic waves Visible light, ultraviolet, infrared, x-rays….. You Try! Convection, Conduction, or Radiation? 1. Your feet get burned when crossing hot pavement barefoot 2. You feel heat from the iron without touching it 3. Your face tingles and feels warm when sitting out in the sun 4. When the heater is running, your room on the second floor feels warmer than downstairs. What are energy conversions? A change from one form of energy to another. Chemical/Potential energy in food is converted into kinetic energy when you are active AND thermal energy to maintain your body temperature. Potential energy of the skater is converted into kinetic energy as he moves down the half-pipe. Energy Conversions in a hair dryer Energy Conservation in Plants Photosynthesis uses energy from the SUN to make new substances that have chemical energy…light energy is changed into chemical energy… Light energy comes from the sun plants change it into chemical energy you body changes it into another chemical energy when you eat it your body changes it to kinetic energy to function Law of Conservation of Energy Energy cannot be CREATED or DESTROYED! It is just converted into other forms of energy. Where does the Energy go?? 1. Friction: force that opposes motion between two touching objects 2. Some energy is transferred into thermal energy Remember the bouncing ball lab?? When you dropped the ball, its bounce height was lower than the original drop height. WHY??? ANSWER… The potential energy at the top was converted to kinetic energy as it dropped. When the ball hit the floor, some of the energy was released as FRICTION and thermal energy from the friction! Some energy also changed into sound energy! Therefore, it didn’t have enough energy to bounce back to its original height.