* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4: Energy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
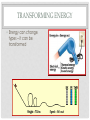
CHAPTER 4: ENERGY SECTION 2: CONSERVATION OF ENERGY WARM UP • A 0.029 kg marble rolls down a ramp. At a height of 0.5 m, its velocity is 3 m/s. • Find the GPE for the marble. • Find KE for the marble. TRANSFORMING ENERGY • Energy can change types – it can be transformed CAN YOU FIND THE ENERGY TRANSFORMATION? Electrical energy is converted to…. Electromagnetic energy (visible light energy) which is converted to…. Mechanical energy (sound energy) which is converted to…. Thermal energy (feel the back of TV or screen sometime) Chemical energy (from gasoline) is converted to… Mechanical energy (engine starts working and moves the car) which is converted to… Sound energy, which is converted to…. Heat energy (don’t touch the engine!) MECHANICAL ENERGY • Mechanical Energy is the total amount of Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy in a system • A system is a group of objects that work together MECHANICAL ENERGY ME = KE + PE ME = ½ mv2 + mgh MECHANICAL ENERGY • For a falling object: • GPE decreases because height decreases • KE increases because gravity increases v MECHANICAL ENERGY • What is the mechanical energy of a 75 kg man on a diving board 10 m above the ground? • The man jumps. After he has fallen 5 m, he is traveling about 9.9 m/s. Find the mechanical energy of the man. LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY • Law of Conservation of Energy: • Energy is never created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed * The total amount of energy in a closed system never changes CONSERVATION OF ENERGY • Why do we lose mechanical energy? • Friction changes kinetic energy to heat energy, which is lost to the surroundings LOSING KINETIC ENERGY TO FRICTION