* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Energy
Renewable portfolio standard (United States) wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
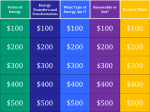
Energy Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. Students will be able to identify various ways which electrical energy is generated using renewable and nonrenewable resources. Students will identify several ways in which energy may be stored. Students will be able to compare how mechanical to electrical energy and electrical to thermal energy is transformed. Students will be able to explain how thermal energy can be transformed by conduction, convection and radiation. Forms of Energy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Thermal Energy the total energy of the particles that make up an object Chemical Energy the energy of a compound that changes as its atoms are rearranged to form new compounds Electrical Energy the energy of moving electrons Sound Energy caused by an objects vibrations Light Energy produced by the vibrations of electrically charged particles Nuclear Energy the energy associated with changes in the nucleus of an atom Homework Complete “Forms of Energy” Packet on the back of the packet draw a tree map with examples of the each type of energy (at least 2 examples each) Due tomorrow Forms Of Energy Thermal Energy Examples Chemical Energy Examples Electrical Energy Examples Sound Energy Examples Light Energy Examples Nuclear Energy Examples Nonrenewable/Renewable Resources 1. Energy-the ability to do work (power) 2. Source-where something comes from 3. Work that occurs when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the source 4. Work and Energy are expressed in the same units Joules (J) What do you think? Nonrenewable Fossil fuels Nuclear power Renewable Heat from within earth Plant waste water Sun Wind Minerals Homework Complete “Energy, Renewable and Nonrenewable Forms” packet Due tomorrow Potential and Kinetic Energy Watch Physical_Science_Motion Video 18 minutes **During video you should be able to define potential and kinetic energy, write in notebook** Definitions Kinetic Energy -energy of motion Potential Energy- energy an object has because of its position or shape Mechanical Energy = Potential Energy + Kinetic Energy Homework Complete “Why Do Basketballs Bounce? Why Do Eggs…Not? Due Tomorrow **Also bring basketballs, tennis balls and rubber balls from home for an experiment NO HOMEWORK NO EXPERIMENT Bounce Experiment 1. Copy the tree map in science notebook for experiment 2. Make hypothesis and write down Bounce Experiment Hypothesis Type of Surfaces Surface 1: Carpet Surface 2: grass Surface 3: Concrete Measurements of how high ball Bounced Bounce Experiment ?’s 1. On which surface did the ball bounce the highest? Why? 2. On which surface did the ball bounce the lowest? Why? 3. What is the purpose of this experiment? 4. What did you learn from this experiment about Potential and Kinetic energy? Energy Conversions 1. Energy Conversions= a change from one form of energy into another 2. Example: a. At what point does the rollercoaster have the greatest kinetic energy? b. At what point does the rollercoaster have the greatest potential energy? Examples of Conversions Alarm Clock Battery Electrical Chemical Light bulb Electrical Blender Electrical Electrical Kinetic and sound Light and Thermal Light and Sound Conservation of Energy 1. Friction=a force that opposed motion between two surfaces that are touching 2. Law of Conservation of Energy=energy can be neither created nor destroyed