* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy and its forms
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Compressed air energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
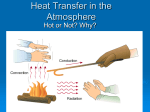
Energy Energy Is defined as the Ability to do Work Energy has Two Types: Kinetic (Energy of Motion) and Potential (Stored Energy) Kinetic Energy KE = ½ m v 2 Ex: A moving car has the ability to do work on the light pole if it hits it. Potential Energy 2 possibilities Gravitational PE Object lifted to some height Elastic PE - A stretched or compressed object (spring or rubber band) Gravitational Potential Energy or Will it fall? GPE = m g h m is the mass of the object in Kg, g is the acceleration due to gravity which is 9.8 m/s2 on earth and h is the height in meters Use the formula page! PE = mgh 41 What is the potential energy of the rock? A 59,900 joules m = 95 kg g = 9.8 m/s2 B 64,600 joules h = 100 m C 93,100 joules 2 x 100 = 95Dkg121,600 x 9.8 m/s joules 93,100 joules C Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy can change forms, but is never created nor destroyed • Loss in one form = gain in an another form • A falling object speeds up as it falls to the ground; PE decreases as KE increases. The KE it has at impact = the PE it had before it fell. Example: A falling object speeds up as it falls to the ground; PE decreases as KE increases, the KE it has at impact with the ground is equal to the PE it had before it fell Energy can be conserved in Non-Mechanical forms The chemical energy in a battery transforms into electrical energy Any reaction where more energy is given off than is used to start it is Exogonic An Endogonic reaction absorbs energy and causes cooling Electrical Energy Moving electrons in a path is electricity • Electrical Potential Difference (v) is measured in Volts • The rate of moving electric charges, Electric Current (I), is measured in Amperes • Resistance or opposition to the movement of the energy is called Resistance (R). Thermal Energy A body contains internal KE due to the motion of its atoms ( they are constantly wiggling and jiggling) Thermal Energy is the total internal KE of a body Temperature is the average KE of a body Heat- Transfer of Thermal Energy Three forms of heating: 1. Conduction-direct contact, a pot heating on a stove (solids) 2. Convection- heating by circulating fluids, (gas and liquid) heating from a fireplace And. . . 3. Radiation – Transfer of Electromagnetic (E.M.) Energy • Objects are heated when exposed to infrared radiation • The suns heats the earth by sending infrared radiation along with other forms of E.M. energy 3.0 x 108 meters through empty space Heat moves by conduction in solids since the particles are close together and vibrate. . . 43 Heat convection occurs in gases and liquids. Heat convection does not occur in solids because solids are unable to — A absorb heat by vibrating B transfer heat by fluid motion C emit radiation by reflecting light D exchange heat by direct contact Solids do radiate heat to their surroundings 2 The primary way liquids and gases transmit heat is by the process of — F reflection G conduction H radiation J convection Fluid heat movement is convection. Fluid motion occurs in liquids and gases. 50 A solar heater uses energy from the sun to heat water. The heater’s panel is painted black to — Convection is movement of heat in fluid matter, heat loss improve emission radiation would be from a solid exterior –infrared Not Gits Painting aF substance will notofchange conductivity – G reduce the heat lossItby convection currents That is a property of metals. would have to be made of H improve absorption of that: infrared radiation a different substance to change Not J J reduce the heater’s conducting properties Emission is giving off – we want to absorb: Not F