* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Heat Transfer
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
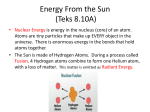
Types of Heat Transfer 1 Heat • The movement of thermal energy from one place to another due to a difference in temperature. • In other words, heat travels from a hot area towards a cold area. 2 On page 7 of your Interactive Notebook, draw the demonstration with food coloring and hot a cold water. • In which beaker is the food coloring spreading out the fastest? • Why does the food coloring spread out faster in one beaker than the other? • Beneath your diagram, describe what happened. 3 Radiation • The movement of heat by invisible waves, so one can feel the heat without touching the object. 4 Convection • Takes place in fluids such as liquids or air. • Occurs when hot air or liquid rises and cold air or liquid moves in to take its place. 5 Conduction • Takes place when heat moves from one area of an object to another area of the object without the object itself moving. 6 Types of Heat Transfer • Conduction • Convection • Radiation 7 8 Examples of conduction • A spoon being heated up while in a bowl of soup. • A car engine heating up. • Your butt warming up the seat of your chair. 9 10 Which objects make good conductors of heat? • Metals • Glass 11 Which objects make poor conductors of heat? • Styrofoam • Wood • Air and fluids 12 Examples of radiation • Heat from the sun warming your body. • Heat from a fire warming your hands. 13 14 Examples of convection • Heating up a pot of soup. • Warm air coming out of the vent in your house and heating up your room. 15 16 Heat transfer animation • http://www.wisconline.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=SC E304 17 Since heat moves from place to place, heat in the atmosphere moves around on the Earth. This causes changes in weather. 18 19 Convection currents 20 Ever notice how it is hotter upstairs than downstairs? Ever wonder why hot air balloons float? It is because hot air rises. 21 22 Convection in our atmosphere 23 Radiation 24 Exit Ticket-Heating the Atmosphere A. B. C. Adapted from: Prentice Hall: Science Explorer, Weather and Climate 25