* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nonrenewable Energy
Renewable portfolio standard (United States) wikipedia , lookup
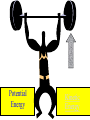
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
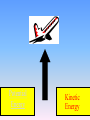
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Click here to begin the activity. Energy Basics • Energy Is the Ability To Do Work Energy is in everything. We use energy for everything we do, from making a jump shot to baking cookies to sending astronauts into space. Energy comes in different forms • • • • • • • Heat (thermal) Light (radiant) Mechanical (motion) Electrical Chemical Nuclear energy sound Potential • Mechanical (motion) Electrical • Chemical • Nuclear energy Kinetic • Heat thermal •Light (radiant) •Mechanical (motion) Electrical Nuclear energy •sound There are two types of energy • Stored (potential) energy • Working (kinetic) energy • For example, the food you eat contains chemical energy, and your body stores this energy until you use it when you work or play Click your mouse to begin. •Decide whether each slide is an example of potential or kinetic energy. •Click on your answer to see if you are correct. Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Energy Sources • Energy sources are divided into two groups — renewable (an energy source that can be easily replenished) and nonrenewable (an energy source that we are using up and cannot recreate). • Renewable and nonrenewable energy sources can be used to produce secondary energy sources including electricity and hydrogen Renewable energy sources include: • Solar energy from the sun, which can be turned into electricity and heat • Wind • Geothermal energy from heat inside the Earth • Biomass from plants, which includes firewood from trees, ethanol from corn, and biodiesel from vegetable oil • Hydropower from hydroturbines at a dam Alternative Energy Sources: • These renewable energy sources are sometimes called alternative energy sources • Solar • Water • Wind Nonrenewable Energy • We get most of our energy from nonrenewable energy sources, which include the fossil fuels — oil, natural gas, and coal. • They're called fossil fuels because they were formed over millions and millions of years by the action of heat from the Earth's core and pressure from rock and soil on the remains (or "fossils") of dead plants