* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Energy?
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
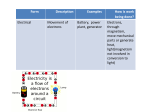
What is Energy? Energy is the ability to A. Do Work B. Cause Change C. Speed D. Accelerate Two Types of Energy Are: Potential Energy •The energy an object has because of where it is or its shape. Kinetic Energy •The energy of motion. Forms of Energy Light Heat Electric Sound Atomic Chemical Mechanical Heat Energy • A form of energy whose source is the motion of molecules. When something is heated, the atoms or molecules in it begin to move faster. The hotter an object is, the quicker its molecules are moving. Heat can travel in 3 ways! Light Energy • Light is electromagnetic energy. It can travel through air and other transparent substances, and through empty space. Light travels at the fastest speed ever measured: 186,000 miles per second. Sound Energy • All sounds are made by something vibrating rapidly back and forth. Sound travels through air at a speed of 750 miles per hour. Electrical Energy Mechanical Energy • This is the energy of motion. The wind, cars moving, riding a bike, and even sound are all examples of mechanical energy. Chemical Energy Nuclear/Atomic Energy • This is the energy found inside the atom. The sun carries on a nuclear reaction all the time releasing amounts of energy. Nuclear power plants generate electricity.