* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lymphatic System PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
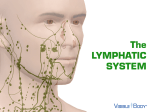
The Lymphatic System Lymph Straw-colored fluid (similar to plasma) INTERSTITIAL FLUID or tissue fluid because it is in the spaces between cells Composed of H2O, lymphocytes, some granulocytes, O2, digested nutrients, hormones, salts, CO2 and urea. Lymph NO red blood cells or protein molecules (too large) Carries digested food, O2 and hormones to cells Carries wastes back to capillaries for excretion Since the lymphatic system has no pump, skeletal muscle action squeezes lymph along Valves prevent backward flow Function of Lymph LYMPH – fluid that goes between capillary blood and tissues Lymph flows only in one direction – from body organs to the heart. Lymph Vessels Closely parallel veins Located in almost all tissues and organs that have blood vessels Tissue lymph enters small lymph vessels which drain into larger vessels called lymphatics – they flow into one of two large, main lymphatics – the THORACIC DUCT and right lymphatic duct. FUNCTION OF LYMPH VESSELS – transport excess tissue fluid back into circulatory system. Lymph Drainage THORACIC DUCT gets lymph from left side of chest, head and neck, abdominal area and lower limbs left subclavian vein superior vena cava heart. RIGHT LYPHATIC DUCT gets lymph from right side of chest, head, neck, and right upper extremity right subclavian vein superior vena cava heart. Tiny, oval shaped - size of pinhead to size of almond Some are located alone but most are grouped (submandibular, cervical, axillary, inguinal, etc.) Site for white cell production and filter for screening out harmful substances If substance can’t be destroyed, node becomes inflamed Lymph Nodes Inflamed Lymph Node Function of Lymph Nodes LYMPH NODES – produce lymphocytes, filter out harmful bacteria. Masses of lymphatic tissue that produce lymphocytes and filter bacteria – they get smaller in size as person gets older PALATINE TONSILS – sides of soft palate ADENOIDS – tonsils on upper part of the throat LINGUAL TONSILS back of the tongue Tonsils Spleen Sac-like mass of lymphatic tissue – largest lymphoid organ in the body Upper left abdominal cavity, lateral to the stomach Forms lymphocytes and monocytes Filters blood Stores large amounts of RBCs (over a pint) – contracts during vigorous exercise or loss of blood, to release RBCs Destroys or removes old or fragile RBCs Upper, anterior thorax, above the heart Thymus is also considered an endocrine gland Largest at puberty Forms lymphocytes before birth involved in the development of “TLymphoctes or TCells.” Completes is work by puberty and is replaced by fat (this is called involution) Thymus Gland