* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infectious Mononucleosis Fever Sore Throat
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Fasciolosis wikipedia , lookup
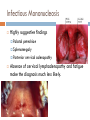
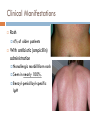
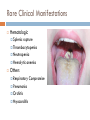
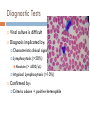
WELCOME APPLICANTS! January 13, 2011 Epstein-Barr Virus Identified in 1964 in Burkitt lymphoma Lab technician became ill with mononucleosis EBV seroconversion Ubiquitous Harbored by nearly all adults No seasonal variation or clustering of cases Epstein-Barr Virus Most infected by oral route “kissing disease” Other modes of transmission Blood transfusions Bone Marrow transplants Sexually transmitted Epstein-Barr Virus Incubation period 30-50 days Age at infection varies with living conditions Age 2 to 3 20% to 80% infected Industrialized More countries: common primary EBV in adolescents IM in 30% to 50% of these cases Infectious Mononucleosis Illness Script Infectious Mononucleosis Fever Sore Throat (exudative pharyngitis) Malaise Lymphadenitis (Cervical) +/- Hepatosplenomegaly Atypical Lymphocytosis Infectious Mononucleosis Highly suggestive findings Palatal petechiae Splenomegaly Posterior cervical adenopathy Absence of cervical lymphadenopathy and fatigue make the diagnosis much less likely. Clinical Manifestations Rash 4% of older patients With antibiotic (ampicillin) administration Nonallergic morbilliform rash Seen in nearly 100%. Benzyl-penicilloyl-specific IgM Rare Clinical Manifestations CNS (5%) Aseptic meningitis Encephalitis Optic neuritis CN palsies Transverse myelitis Guillian-Barre Rare Clinical Manifestations Hematologic Splenic rupture Thrombocytopenia Neutropenia Hemolytic anemia Others Respiratory Pneumonia Orchitis Myocarditis Compromise Diagnostic Tests Viral culture is difficult Diagnosis implicated by: Characteristic clinical signs Lymphocytosis (>50%) Absolute Atypical (> 4500/mL) Lymphocytosis (>10%) Confirmed by: Criteria above + positive heterophile Heterophile Test (Monospot) Heterophile antibodies react to antigens from unrelated species Monospot- Latex agglutination assay using horse erythrocytes and patient serum. Peak levels at 2-6 weeks May remain elevated for up to 1 year Sensitivity 85% Less sensitive in children < age 3. Specificity 100% Diagnostic Testing Other antibody Testing (useful if heterophile negative) anti-VCA Some IgM evidence for active/recent infection anti-EBNA Excludes active primary infection Treatment “Take it easy” No contact sports until spleen no longer palpable Avoid ampicillin and amoxicillin Steroids reserved for most severe of cases Associated Conditions X-linked Lymphoproliferative Disease (XLP) Defect in signaling lymphocytic activation moleculeassociated protein Characterized by Nodular B-cell lymphomas +/- CNS involvement Profound hypogammaglogulinemia Aplastic anemia Severe infectious mono early in life 4% survival Associated Conditions EBV associated B-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disease 10% of transplant recipients Donor organ is common vehicle of EBV infection Occurs early after transplant Time of most severe immunosuppression Other Associated Conditions Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Chronic Active EBV Infection Malignancies Burkitt Lymphoma Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Hodgkin Disease T-Cell Lymphoma Gastric carcinoma