* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dwarf Planets
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Jumping-Jupiter scenario wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
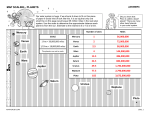
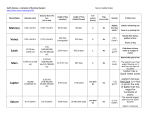
Note that the following lectures include animations and PowerPoint effects such as fly-ins and transitions that require you to be in PowerPoint's Slide Show mode (presentation mode). Chapter 24 Uranus, Neptune, and the Dwarf Planets Guidepost Two planets circle the sun in the twilight beyond Saturn. You will find Uranus and Neptune substantially different from Jupiter and Saturn, but recognizable as Jovian planets. As you explore further you will also discover a family of dwarf planets, including Pluto, which appear to be leftover planet construction material. This chapter will help you answer four essential questions: • How are Uranus and Neptune similar to, and different from, Jupiter and Saturn? • How did Uranus and Neptune, along with their rings and moons, form and evolve? • How is Neptune different from Uranus? • How are Pluto and the dwarf planets related to the origin of the solar system? Guidepost As you finish this chapter, you will have visited all of the major worlds in our solar system. But there is more to see. Vast numbers of small rocky and icy bodies orbit among the planets, and the next chapter will introduce you to these fragments from the age of planet building. Outline I. Uranus A. The Discovery of Uranus B. The Motion of Uranus C. The Atmosphere of Uranus D. The Interior of Uranus E. The Rings of Uranus F. The Moons of Uranus G. A History of Uranus II. Neptune A. The Discovery of Neptune B. The Atmosphere and Interior of Neptune C. The Rings of Neptune D. The Moons of Neptune E. The History of Neptune Outline (continued) III. The Dwarf Planets A. The Discovery of Pluto B. Pluto as a World C. The Family of Dwarf Planets D. Pluto and the Plutinos The Discovery of Uranus Chance discovery by William Herschel in 1781, while scanning the sky for nearby objects with measurable parallax: discovered Uranus as slightly extended object, ~ 3.7 arc seconds in diameter. The Motion of Uranus Very unusual orientation of rotation axis: Almost in the orbital plane Possibly result of impact of a large planetesimal during the phase of planet formation Large portions of the planet exposed to “eternal” sunlight for many years, then complete darkness for many years! 19.18 AU 97.9o The Atmosphere of Uranus Like other gas giants: No surface Gradual transition from gas phase to fluid interior Mostly H; 15 % He, a few % Methane, ammonia and water vapor Optical view from Earth: Blue color due to methane, absorbing longer wavelengths Cloud structures only visible after artificial computer enhancement of optical images taken from Voyager spacecraft The Structure of Uranus’ Atmosphere Only one layer of Methane clouds (in contrast to 3 cloud layers on Jupiter and Saturn) 3 cloud layers in Jupiter and Saturn form at relatively high temperatures that occur only very deep in Uranus’ atmosphere. Uranus’ cloud layer is difficult to see because of thick atmosphere above it. Also shows belt-zone structure Belt-zone cloud structure must be dominated by planet’s rotation, not by incidence angle of sun light! Cloud Structure of Uranus Keck Telescope images of Uranus show clear variability of the cloud structures. Possibly due to seasonal changes of the cloud structures The Interior of Uranus Average density ≈ 1.29 g/cm3 larger portion of rock and ice than Jupiter and Saturn Ices of water, methane, and ammonia, mixed with hydrogen and silicates The Magnetic Field of Uranus No metallic core no magnetic field was expected But actually, magnetic field of ~ 75 % of Earth’s magnetic field strength was discovered: Offset from o center: ~ 30 % Inclined by ~ 60 Possibly due to dynamo in against axis of of planet’s liquid-water/ammonia/methane rotation radius! solution in Uranus’ interior Magnetosphere with weak radiation belts; allows determination of rotation period: 17.24 hr. The Magnetosphere of Uranus Rapid rotation and large inclination deform the magnetosphere into a corkscrew shape. UV images During Voyager 2 flyby: South pole pointed towards sun; direct interaction of solar wind with magnetosphere Bright aurorae! The Rings of Uranus Rings of Uranus and Neptune are similar to Jupiter’s rings. Confined by shepherd moons; consist of dark material Apparent motion of star behind Uranus and rings Rings of Uranus were discovered through occultations of a background star The Rings of Neptune Ring material must be regularly resupplied by dust from meteorite impacts on the moons. Interrupted between denser segments (arcs) Made of dark material, visible in forwardscattered light Focused by small shepherd moons embedded in the ring structure The Rings of Neptune (2) Two newly discovered rings orbit Uranus far outside the previously known rings. Outermost ring is only visible as a segment, following the small moon Mab The Moons of Uranus 5 largest moons are visible from Earth 10 more discovered by Voyager 2; more are still being found Dark surfaces, probably ice darkened by dust from meteorite impacts 5 largest moons all tidally locked to Uranus Interiors of Uranus’s Moons Large rock cores surrounded by icy mantles The Surfaces of Uranus’ Moons (1) Oberon Old, inactive, cratered surface, but probably active past Long fault across the surface Dirty water may have flooded floors of some craters Titania Largest moon Heavily cratered surface, but no very large craters Active phase with internal melting might have flooded craters The Surfaces of Uranus’s Moons (2) Umbriel Dark, cratered surface No faults or other signs of surface activity Ariel Brightest surface of 5 largest moons Clear signs of geological activity Crossed by faults over 10 km deep Possibly heated by tidal interactions with Miranda and Umbriel Uranus’s Moon Miranda Most unusual of the 5 moons detected from Earth Ovoids: Oval groove patterns, probably associated with convection currents in the mantle, but not with impacts 20 km high cliff near the equator Surface features are old; Miranda is no longer geologically active. Neptune Discovered in 1846 at position predicted from gravitational disturbances on Uranus’s orbit by J. C. Adams and U. J. Leverrier Blue-green color from methane in the atmosphere 4 times Earth’s diameter; 4 % smaller than Uranus The Atmosphere of Neptune The “Great Dark Spot” Cloud-belt structure with high-velocity winds; origin not well understood Darker cyclonic disturbances, similar to Great Red Spot on Jupiter, but not long-lived White cloud features of methane ice crystals The Moons of Neptune Two moons (Triton and Nereid) visible from Earth; 6 more discovered by Voyager 2 Unusual orbits: Triton: Only satellite in the solar system orbiting clockwise, i.e. “backward”. Nereid: Highly eccentric orbit; very long orbital period (359.4 d) The Surface of Triton Very low temperature (34.5 K) Triton can hold a tenuous atmosphere of nitrogen and some methane; 105 times less dense than Earth’s atmosphere. Surface composed of ices: nitrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide. Possibly cyclic nitrogen ice deposition and revaporizing on Triton’s south pole, similar to CO2 ice polar cap cycles on Mars Dark smudges on the nitrogen ice surface, probably due to methane rising from below surface, forming carbon-rich deposits when exposed to sun light. The Surface of Triton (2) Ongoing surface activity: Surface features probably not more than 100 million years old Large basins might have been flooded multiple times by liquids from the interior. Ice equivalent of greenhouse effect may be one of the heat sources for Triton’s geological activity. The Discovery of Pluto Discovered 1930 by C. Tombaugh Existence predicted from orbital disturbances of Neptune, but Pluto is actually too small to cause those disturbances Pluto as a World Virtually no surface features visible from Earth ~ 65 % of size of Earth’s Moon Highly elliptical orbit; coming occasionally closer to the sun than Neptune Orbit highly inclined (17o) against other planets’ orbits Neptune and Pluto will never collide. Surface covered with nitrogen ice; traces of frozen methane and carbon monoxide Daytime temperature (50 K) enough to vaporize some N and CO to form a very tenuous atmosphere Pluto’s Moons Moon Charon discovered in 1978; about half the size and 1/12 the mass of Pluto itself Tidally locked to Pluto Two more moons, Nix and Hydra, were discovered in 2006 in a Hubble Space Telescope image. Hubble Space Telescope image Hubble Space Telescope image Pluto and Charon Orbit highly inclined against orbital plane From separation and orbital period: Mpluto ~ 0.2 Earth masses Density ≈ 2 g/cm3 (both Pluto and Charon) ~ 35 % ice and 65 % rock Large orbital inclinations Large seasonal changes on Pluto and Charon The Surface of Pluto No surface features can be directly imaged from Earth. But, brightness variations while Charon moves across Pluto allow the reconstruction of a rough surface map. The Origin of Pluto and Charon Probably very different history than neighboring Jovian planets Pluto and Charon are probably members of Kuiper belt of small, icy objects (see Chapter 25), caught in orbital resonances with Neptune (“Plutinos”). Collision between Pluto and Charon may have caused the peculiar orbital patterns and large inclination of Pluto’s rotation axis Because of its different origin from the planets, Pluto is no longer considered a planet, but is the prototype of a new class of “Dwarf Planets”. The Family of Dwarf Planets • Small, rocky bodies which originated in the Kuiper Belt • Later captured into shorter-period orbits in the realm of the regular planets • Three dwarf planets clearly identified so far: Pluto Eris Ceres The ``10th planet’’: Discovered in 2004 The largest asteroid 4 % larger than Pluto 900 km diameter 27 % more massive than Pluto 70 % further away from the sun than Pluto Typical asteroid orbit between Mars and Jupiter