* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organize Your Space PowerPoint.
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Galilean moons wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
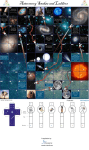
ORGANIZE YOUR SPACE! (in order from larger to smaller) GALAXY CLUSTER Groups of galaxies that are bound together by gravity. Galaxy- Large groupings of stars in space. Our galaxy (the Milky Way) is a spiral galaxy like this one. Spiral Galaxy in Ursa Major The Crab Nebula in Taurus The Great Nebula in Orion Nebula- Huge bodies of dust and gas that are the birthplace of stars The Horse Head Nebula in Orion The Ring Nebula in Lyra GLOBULAR CLUSTER – Groups of 20,000 to 100,000 older stars that look like a ball of stars. They are often located in a spherical halo around galaxies. OPEN CLUSTER – Groups of about a few hundred to a few thousand stars. They may include many young bright blue stars. Solar System – The sun and nine planets and other bodies that travel around the sun. Asteroid Belt – Most asteroids orbit the sun in this area between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter The belt is 180 million km in width and contains thousands of asteroids that are constantly in motion, crashing into each other at high speeds and sending clouds of dust into space. The combined mass of all the asteroids would only be 1/1000 the mass of the earth and if all the asteroids were combined together their diameter would be only half the diameter of our moon. Star (our sun) – A large body of mostly hydrogen and helium gas which releases light energy by nuclear fusion. Planet – a large body composed of either rock (terrestrial) or gas (gas giant) which orbits the sun. They shine by reflecting light from the sun. Moon/Satellite- a body that orbits around a larger body, usually a planet. Planets can have none, one, or more than one of these. Jupiter and two of its 4 Galilean moons (Io, Europa, Callisto, Ganymede). Earth’s moon Jupiter’s 4 Galilean moons Asteroid – Small rocky bodies that orbit the sun. They range in size from a few meters across to more than 900 km. Meteoroid – a rocky body smaller than an asteroid that orbits the sun. They are really bits of dust or rocks from space. They can get pulled in by earth’s gravity into our atmosphere. Once they enter our atmosphere If they don’t burn up they are called meteors (“shooting stars”) and land on earth they are called meteorites. How Did You Do? • • • • • • • • • • • • • Universe Galaxy Cluster Galaxy Nebula Globular Cluster Open Cluster Solar System Asteroid Belt Star (Our Sun) Planet Moon/Satellite Asteroid Meteoroid