* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun - Colina Middle School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
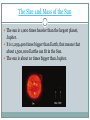
The Sun BY MARCELLA GIUFFRIDA & GRACE HILTON Key Terms • Nuclear fusion - a nuclear reaction where nuclei of low atomic numbers fuse to form a heavier nucleus with the release of energy. • Core - the central or most important part of something • Helium - an inert gas that is the lightest member of the noble gas series. • Hydrogen - a colorless, odorless, highly flammable gas Key Terms • Energy - power taken from physical or chemical resources, especially to provide light and heat or to work machines. • Radiative zone – a region of very tightly packed gas where energy is transferred mainly in the form of electromagnetic radiation. • Convection zone – the outermost layer of the sun’s interior. Nuclear Fusion The sun produces energy through nuclear fusion. During nuclear fusion, two atomic nuclei combine, forming a larger and more massive nucleus and releasing energy. It can only occur under high pressure and high temperature. The mass of helium produced is slightly less than the mass of hydrogen put into it. The missing mass is changed into energy. The Core The conditions at the core of the sun are unbearably extreme. The temperature is approximately 15.6 million Kelvin, and the pressure is 250 billion atmospheres. The sun’s core is the source of all the sun’s energy. The temperature and pressure are so high that nuclear fusion can take place. The sun’s core has a diameter of 400,000 km, more than 30 times the earth’s diameter. Structure of the Sun The photosphere is the visible surface of the sun, this sphere gives off the visible light that we see. The chromosphere is the layer that gives the sun its color. The corona is essentially the “halo” around the sun, it extends into space for millions of kilometers. Structure of the Sun Eventually the corona will thin out into streams of electrically charged particles called Solar wind. Sunspots are areas of gas on the surface of the sun, these spots are cooler areas of gas, they don’t give off as much light as the rest of the surface of the sun. That is why they show up darker in pictures. The Size and Mass of the Sun The sun is 1,000 times heavier than the largest planet, Jupiter. It is 1,299,400 times bigger than Earth, that means that about 1,300,000 Earths can fit in the Sun. The sun is about 10 times bigger than Jupiter. The Sun’s Gravitational Effects Gravity and outward pressure are balanced throughout the sun. Those forces combine to produce the sun’s spherical shape. The sun’s gravitational pull keeps the planet in line on their orbital path. The planets orbit the sun because the lighter object orbits around the heavier object. Planet Diagram of the Structure of the Sun Radiative Zone The energy that is produced in the sun’s core moves out through the middle layer of the sun, the radiative zone. The radiative zone is a region of very tightly packed gas, energy is transferred mainly in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The radiative zone is very dense so energy can take more than 100,000 years to move through it . The Sun’s Interior – Convection Zone The convection zone is the outermost layer of the sun’s interior. Hot gases rise from the bottom of the (convection zone) and cool as they reach the top. Cool gases drop, forming rings of gas that transport energy to the sun’s surface. StoryBots Video Sun Quiz 1. a) How does the sun produce energy? through the light beams b) through nuclear fusion c) through hydrogen d) through the moon Sun Quiz 2. Nuclear fusion can only occur under: a) low pressure and high temperature b) high pressure and low temperature c) high pressure and high temperature d) low pressure and low temperature Sun Quiz 3. What gives the sun its color? a) the hue layer b) the chromosphere c) the corona d) sun spots Sun Quiz 4. The _______ zone is a region of very tightly packed gas. 5. The _______ zone is the outermost layer of the sun’s interior. 6. The _______ is the “halo” around the sun. Sun Quiz 7. The conditions at the core are a) very cool b) room temperature c) extremely unbearable d) under 100 degrees Fahrenheit Sun Quiz 8. True/False: the conditions in the sun’s core are only slightly warmer than Earth’s temperature. 9. True/False: the sun’s core is the source of all the sun’s energy. 10. True/False: the sun produces helium through nuclear fusion.