* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
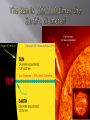
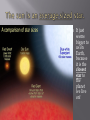
By Miss O. Remember “solar” means “things having to do with the sun (in Latin). The asteroid belt is the region of the Solar System located roughly between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter. An asteroid is a large rock in outer space. Some, like Ceres, can be very large, while others are as small as a grain of sand. Halley’s Comet is the best-known of the short-period comets, and is visible from Earth every 75 to 76 years. We will see it again in 2062. a celestial body moving about the sun, usually in a highly eccentric orbit, consisting of a central mass surrounded by an envelope of dust and gas that may form a tail that streams away from the sun. a transient fiery streak in the sky produced by a meteoroid passing through the earth's atmosphere; also known as a shooting star It just seems bigger to us on Earth, because it is the closest star to the planet we live on! Remember: rotate means “spin on its axis.” Yellow stars are made of gases: hydrogen and helium. In the form of heat and light. The energy comes from the fusion of atoms. The sun is the source of most of the energy on Earth. 1. Corona 2. Chromosphere 3. Photosphere *Convection Zone *Radiation Zone 4. Core Reaches far out into space Latin word for “crown” It is seen as a glow around the sun during a solar eclipse. Streams of particles are called “solar wind.” 2000-3000 km thick. When it can be seen it is reddish in color This color is the origin of its name (chromos meaning ``color''). The faint flow of the chromosphere is due to an emission spectrum from hot, low density gases emitting at discrete wavelengths. “sphere of light” It is the part of the sun that we can see. “surface of the sun” Convective or Convection Zone Radiative zone spreads and heats atomic particles These gas particles “boil” Radiative or Radiation Zone Energy from the core heats just like a radiator heats the air in a room 27 million degrees Fahrenheit ! The center of the sun Very, very hot At the core, gravity pulls all of the mass inward and creates an intense pressure. The pressure is high enough to force atoms of hydrogen to come together in nuclear fusion reactions -something we try to mirror here on Earth.