* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hinduism - John Bowne High School
Indra's Net (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hindu nationalism wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Invading the Sacred wikipedia , lookup
Akhil Bharatiya Hindu Mahasabha wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Daṇḍa (Hindu punishment) wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
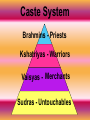
Hinduism Copyright © Clara Kim 2007. All rights reserved. Aim: How did the central ideas of Hinduism affect the people of India? • Do Now: Copy the Vocabulary • Polytheism: the belief in many gods • Reincarnation: the belief that all souls are reborn after death (return as something else) • Dharma: the religious obligations of a Hindu, includes fasting, self-denial, and non violence • Karma: the judgment of one’s soul after death. Those who have good karma come back as a higher life form • Moksha: State of perfect understanding of all things and release from life in this world Reading Activity • Students will be chosen to read passages from the documents • While your classmates are reading, please underline all words you do not understand (we will discuss these words as a class) • After reading the documents, you will answer the questions that follow Student Debrief Students will take notes using the Hinduism handout Lets Take a Hindu Start • Rise early and bathe in the Ganges River –Cleansing body and soul Lets Take a Hindu Start • Burn incense and offer prayer Lets Take a Hindu Start • Yoga – breathing exercises Background • No real founder • No formal church • Almost considered a way of life Aryan Invaders • Aryans and nonAryans followed their own forms of religion • This resulted in the blending of different forms of the religion Polytheistic? Monotheistic? • One god or world soul = Brahman –He has three personalities 1.Brahma – the creator •Vishnu – The Preserver • Shiva – The Destroyer Vedas • Collection of sacred writings –Hindu teachers try to interpret and explain the meaning of the Vedic hymns The Upanishads • Teachers’ asked questions as they meditated –Later the teachers’ comments were written down in the Upanishads Moksha • State of perfect understanding of all things and release from life in this world Reincarnation • Means ‘Rebirth’ • An individual spirit (ATMAN) is born again and again until Moksha is achieved Karma • Means good or bad deeds • Your Karma determines your state of reincarnation Summary Activity • Students will take out the handout “What are the central beliefs of Hinduism?” • Students will read the documents and answer the questions based on the information we have learned today Aim: How did the caste system organize Hindu society? • Do Now: Copy the vocabulary into your notebook • Caste System: system where people are ranked into groups based on heredity • Brahmin: priest class • Vaisyas: herders, farmers, merchants • Sudras: servants, laborers • Untouchables: performed the lowest tasks in society Caste System Brahmins - Priests Kshatriyas - Warriors Vaisyas - Merchants Sudras - Untouchables Recall Activity Homework Check Discuss homework Document Activity 1) Students will read or analyze the first (2) documents 2) After, students will answer the questions that follow 3) We will then discuss your findings Reading Activity • As a class we will read the documents relating to the treatment of the “untouchables” • At the end of each document, students will report on how the untouchable is treated Caste System • Began in the Hindu religion and is based on writings in the Vedas (holy book) • Rules: • 1) a person was born into their caste and could not change it during their life, only in their next reincarnated life. Only after following caste rules would bring good karma • 2) different caste members were not allowed to intermarry or work together • 3) untouchables were considered so “unclean” that they were outside the caste system (outcasts) Pictures Cited • • • • • • • • Slide 1 – http://www.unitedindia.com/INDEX_files/Hindu_Om_Aum.jpg Slide 2 – http://www.cardsunlimited.com/largeimage/SaddhuatGanges.jpg Slide 3 – http://www.shantishop.com Slide 4 – http://www.harunyahya.com/images_books/images_buddhism/budizm36.jpg, http://blog.insideoutmag.com/outabout/Incense%20at%20Hindu%20temple.png Slide 5 – http://www.webwombat.com.au/lifestyle/health/images/yoga-1.jpg, http://gymnasticscoaching.com/wp-content/uploads/2007/07/yoga.jpg Slide 6 – www.theholidayspot.com Slide 7 – http://www.chemistryland.com/CHM107Lab/Syllabus/blender.jpg Slide 8 – http://content.answers.com/main/content/wp/en/thumb/4/4d/250px-Trimurti.jpg Slide 9 – http://www.hknet.org.nz/brahma.jpg • Slide 10 – www.umysl.pl/astrolog/iko_bogowie/vishnu.jpg • Slide 11 – http://www.monochrom.at/polytheism/pictures/TanzenderShiva.jpg • Slide 12 – http://blog.shunya.net/photos/uncategorized/2007/10/23/vedas_2.jpg • Slide 13 – http://lunaydragon.files.wordpress.com/2007/05/vedas2.jpg • Slide 14 – http://www.siliconindia.com/books/newbooks/Pics/Upanishads_BIG.jpe • Slide 15 – http://cci.wl.dvgu.ru/news/images/bigfoto/moksha.jpg • Slide 16 – www.hknet.org.nz/changing-bodies2.jpg • Slide 17 – http://www.spiritandsky.com/images/reincarnation2.jpg • • Slide 18 – www.smart-kit.com Slide 19– made •