* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download It is a way of life which shapes and unifies much of Indian
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Dharmaśāstra wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Invading the Sacred wikipedia , lookup
Indra's Net (book) wikipedia , lookup
Daṇḍa (Hindu punishment) wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Malaysia wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
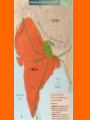
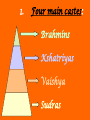
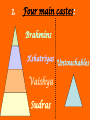
Hinduism Hinduism is the chief religion of India (85% of population). It is a way of life which shapes and unifies much of Indian culture. Om—symbol of Hinduism I. Hinduism is a collection of beliefs which developed over a long period of time. 1. Founder – can’t be traced to one founder 2. Holy Texts: a. Vedas – Four collections of prayers, magical spells and instructions for performing rituals. b. Upanishads – (oo PAN ih shadz) text which helps to explain the ideas contained in the Vedas 3. Beliefs: a. Reincarnation – rebirths - repeated passing of the soul from one life to the next b. Karma – an individual’s good or bad deeds— follows you from one reincarnation to another *Influences what you come back as in your next life c. Moksha – a state of perfect understanding of all things—release from this world II. Caste system: social classes developed in ancient times and believed to be based on occupation 1. Four main castes: Brahmins Kshatriyas Vaishya Sudras 1. Four main castes: Varnas or social classes a. Brahmins – religious class of priests b. Kshatriyas – rulers and warriors c. Vaishya – landowners and merchants d. Sudras – peasants and laborers 1. Four main castes: Brahmins Kshatriyas Vaishya Sudras Untouchables 2. Harijians – Untouchables – outcasts in Hindu society. They are usually poor and less educated then other Hindus. a. Mahatma Gandhi – greatly improved the lives and status of the Untouchables in Indian society. 3. Born into a caste for life and determines occupation, who you may marry and who you can associate. In other words, EVERYTHING! 4. Today, there are hundreds of subdivisions of the caste system. 5. Dharma – duties and obligations that each caste must follow. 6. Karma (deeds or actions) determines your caste III. Gods – Polytheistic ! 1. Brahman– World Soul that is made up of 3 gods: a. Brahma: the creator b. Vishnu: the protector c. Shiva: the destroyer IV. Holy Sites: 1. The Ganges River is a holy site for Hindus. All Hindus are expected to visit and bath in the Ganges River once in their lifetime. Ganges River Taj Mahal Mumtaz Muhal Shah Jahan Tombs of Shah Jahan and Mumtaz Muhal