* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Rajan Zed prayer protest wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-Hindu law wikipedia , lookup
Daṇḍa (Hindu punishment) wikipedia , lookup
2013 Bangladesh anti-Hindu violence wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu nationalism wikipedia , lookup
1950 East Pakistan riots wikipedia , lookup
Invading the Sacred wikipedia , lookup
Akhil Bharatiya Hindu Mahasabha wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Malaysia wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Vishishtadvaita wikipedia , lookup
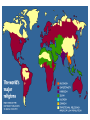
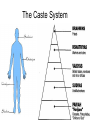
• Focus Points • • • • Where: Based in India 900 Million followers When: Began circa 1500 B.C. Sacred texts: Vedas (among many others) • Many forms of Brahman • Reincarnation/karma/moksha • Indian caste system Where are the Religions? Do Now Who are the Aryans? Pg 37 • Nomadic peoples who moved into India circa 1500 B.C. • From them grows Hinduism. Do Now Describe the caste system – How did the Hindu belief system offer a way out of the caste system? Caste System • Set of rigid social classes • No mobility until death (reincarnation) • Karma determined how you would be reborn Samsara – cycle of life, death, and rebirth Hinduism Symbol - Om • Hindus begin their day or any work or a journey by uttering Om. Om represents “Brahman”. Their god takes many different forms. Location Where It Began • Cannot be traced to any one individual. But it begins in India with the beliefs of the Aryan people. • The earliest of the Hindu scriptures – The Vedas – was composed by the Aryan priests The term "Hindu" was introduced by foreigners who referred to people living across the River Indus or Sindhu, in the north of India. Structure Monotheistic? There are thousands of various forms of a single Supreme Being = Brahman. Religious Figure • Hindus also worship spirits, trees, animals and even planets. • Cows are a sacred animal, they represent all living creatures. Many Hindus are vegetarians. Brahma :creator Vishnu: The Preserver The Hindu Trinity Vishnu: The Preserver Brahma :creator Shiva: The Destroyer All these deities are forms of the Brahman Ganesh: remover of obstacles Holy Book • The basic scriptures of Hinduism, are the Vedas (sometimes called the Rig Veda). • Two types of sacred writings comprise the Hindu scriptures: "Shruti" (heard) and "Smriti" (memorized). They were passed on from generation to generation orally for centuries before they were written down mostly in the Sanskrit language. The Caste System Beliefs • • • • • Reincarnation – individual soul is reborn in a different form after death Samsara – Repeating cycle of life and death Karma – right action in life – determines rebirth The goal is to achieve oneness with god, Brahman – a union. atman – the individual self – is the Brahman that is part of everyone. This is what is united with Brahman through strict practice Samsara =(rebirth) Reincarnation Moksha =(liberation from the cycle of Samsara/Reincarnation) • Mahatma Ghandi (1869-1948) is NOT a Hindu god, but is a famous Hindu. His use of non-violent resistance led to India’s independence from Britain (1942) and inspired Martin Luther King to use the same technique in American Civil Rights movement.