* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tutorial: What Software Lawyers Need to Know about Software
Falcon (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Design Patterns wikipedia , lookup
Comment (computer programming) wikipedia , lookup
Structured programming wikipedia , lookup
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Java (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Abstraction (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
C Sharp syntax wikipedia , lookup
Name mangling wikipedia , lookup
Software quality wikipedia , lookup
Program optimization wikipedia , lookup
History of compiler construction wikipedia , lookup
Java ConcurrentMap wikipedia , lookup
Java performance wikipedia , lookup
Software bug wikipedia , lookup
C Sharp (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
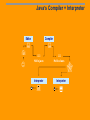
Software - 1960s to 1970s Computer software is customdeveloped Most computer systems are large and have unique configurations Languages are procedural (FORTRAN, COBOL, BASIC, C) A computer system costs $100K and up Source code is usually delivered Software - 1980s Development of DOS/Wintel platform PCs become ubiquitous and standardized Software becomes an off-the-shelf product Source code is not delivered Software - 1990s to 2000s "Free software" movement / opensource Rise of object-oriented programming (e.g. C++, Java) Rise of distributed computing: client-server technology and web servers/Java Software - 2010s + Cloud/web applications Mobile / responsive design Niche/business market products Mass consumer free. Software Development 1950-1960's: Emphasis on efficiency fast algorithms small program size limited memory use Now: Emphasis on programmer’s productivity team development reusability of code easier maintenance Often cryptic code Not user-friendly Upgradability Better documented User-friendly Programming Languages Assembly languages 1940 1950 C C# LISP Scheme Logo 1960 1970 Fortran Machine code C++ 1980 Pascal Java 1990 2000 Python Basic Smalltalk Smalltalk-80 Top Computer Languages 2014 Source Code, Binary Code, and Compilers Source Code Written in “Higher Level Computer Language“ Trained programmer can read, understand, critique, edit and Improve Computer CANNOT use in this form Designed to show logic and structure Compiler Software Converts source to machine-readable form Strips out human-readable comments and logic Results in Binary Code - “1’s and 0’s” Machine Code Executable by computers Used in binary or “object” form Conventional form of distributed proprietary software Programs written in some languages need not be compiled to be read by a computer (e.g., BASIC, PHP, HTML,JAVASCRIPT) Java’s Compiler + Interpreter Editor Compiler : : 7 K Hello.java Hello.class Interpreter Interpreter : Hello, World! Why Bytecodes? Platform-independent Load from the Internet faster than source code Interpreter is faster and smaller than it would be for Java source Source code is not revealed to end users Interpreter performs additional security checks, screens out malicious code Types of Programs Console applications Applets GUI applications Web Services Console Applications Simple text dialog: prompt input, prompt input ... result C:\javamethods\Ch02> path=%PATH%;C:\Program Files\Java\jdk 1.5.0_07\bin C:\javamethods\Ch02> javac Greetings2.java C:\javamethods\Ch02> java Greetings2 Enter your first name: Josephine Enter your last name: Jaworski Hello, Josephine Jaworski Press any key to continue... GUI Applications Menus Clickable panel Buttons Slider OOP — Object-Oriented Programming An OOP program models a world of active objects. An object may have its own “memory,” which may contain other objects. An object has a set of methods that can process messages of certain types. OOP (cont’d) A method can change the object’s state, send messages to other objects, and create new objects. An object belongs to a particular class, and the functionality of each object is determined by its class. A programmer creates an OOP application by defining classes. Inheritance A programmer can define hierarchies of classes More general classes are closer to the top Person Child Baby Toddler Adult Teen OOP Benefits Facilitates team development Easier to reuse software components and write reusable software Easier GUI (Graphical User Interface) and multimedia programming