* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Muscles - Cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
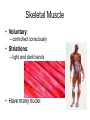
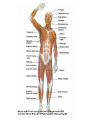
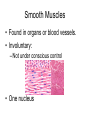
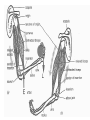
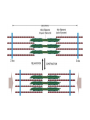
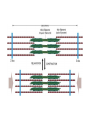
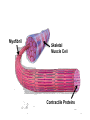
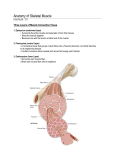
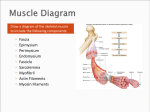
Muscles Skeletal Muscle • Voluntary: – controlled consciously • Striations: – light and dark bands • Have many nuclei Smooth Muscles • Found in organs or blood vessels. • Involuntary: – Not under conscious control • One nucleus Cardiac Muscle • Found on the heart. • One or two nuclei. • Involuntary control. Flexor • Bends the bone at the joint. • Ex: Bicep Extensor • Makes the bone straighten at the joint. Muscle Contraction (Microscopic) • Myofibril: – Small fibers found within the cells of muscles. – *Myofibrils are made of two type of filaments. Actin Filaments • Thin filaments made of a protein called actin. Myosin Filaments • Thick filaments made of a protein called myosin. Muscle Contraction Step #1 • Actin filaments are stimulated to slide over the myosin filaments. • ** The heads of the myosin filaments connect to the actin and pivot. This causes them to slide. Muscle Contraction Step #2 • When the actin filaments slide the length of the sarcomere becomes shorter. Muscle Contraction Step #3 • When the sarcomeres become shorter this causes each myofibril to become shorter. Myofibril Skeletal Muscle Cell Contractile Proteins Muscle Contraction Step #4 • When each myofibril becomes shorter it causes the muscle fibers to become shorter. Muscle Contraction Step # 5 • When each muscle fiber shortens the overall muscle contracts. What Stimulates a Muscle? 1. Contractions are coordinated with your nervous system: motor neurons. 2. A stimulated neuron will cause the release of calcium in the muscle. 3. Calcium causes the interaction between the myosin and actin filaments.