* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nerves and glials - Central Connecticut State University
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
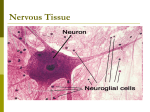
New Hope for Hurt Neurons • Is there recovery after damage to the spinal cord or brain? • Can stem cells be used to reconstruct broken pathways? • A few years ago, the stuff of myths. • Perhaps a reality Christopher Reeve as Superman Christopher Reeve Paralysis Foundation www.paralysis.org Reeve’s Goal To Stand and Raise a Glass on 50th Birthday. 9/25/2002 Traditional Divisions KW 2-13 Functional Divisions KW 2-13 CNS and PNS KW 1-2 Brain in Skull KW 2-1 CNS and PNS (sketch) Brain Spinal cord Nerves (PNS) Skull Vertebrae Neurons and Glial Cells KW 2-12 Neuron KW 3-3 Types of Neurons KW 3-7 Neuron (detail) KW 3-5 Neuron (info flow) KW 3-6 Types of Glial Cells KW 3-1 Glial Cell Functions • • • • Supportive glial = glue Nutrition Waste disposal “vacuum cleaners” Insulate neurons Neurons vs Glial Cells • Neurons • Transmit message. • Mature cells don’t replicate. • Dead cells are not replaced. • Glial cells • Supportive role. • Mature cells do replicate. • Dead cells are replaced. CNS and PNS Myelin Astrocyte KW 3-9 Myelin Wrap CNS PNS Myelin Sheath in PNS Schwann Cells in PNS Axon Myelin Sheath Schwann cell beakdown KW 3-11 Schwann Cell Recovery KW 3-11 Combo Schwann KW 3-11 Can axons regrow in CNS? • Yes, but their path is blocked by CNS Glial Cells. • CNS Glial cells (Oligodendrocytes) form scar tissue. • Pathway is blocked by scar tissue. scar CNS Solutions • • • • Block scar tissue from forming. Schwann cell bridges (Lars Olson). Spinal motor pathways cut in rats. Loss control of hind limbs. Other CNS Solutions • • • • • Nerve growth factors. Stem cell implants. Quick response to spinal cord injury. “Golden Hour” = first hour after injury. Prevent further damage. Rapid Response to Injury • • • • • Steroids to reduce swelling. Provide support. Cord usually not severed. Relieve pressure. Stabilize vertebrae. Recovery from injury • Drugs to help remaining neurons function better. • Retrain body to use back-up systems. • Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): a computer assisted movement system Functional Electrical Stimulation Hand Grasp in Operation Spinal Cord Outcomes • 12,000 new cases a year • Most young men. • 90% survive accident. • Lifetime disability • Greater hope for recovery.