* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The End of War in Europe
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Ursula Kuczynski wikipedia , lookup
War Front: Turning Point wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
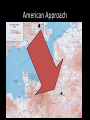
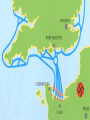
The End of WWII in Europe • Ending WWII in Europe – “The Fall” Clips • Nuremburg How to PWN the documents • Close analysis! (NOT JUST RESTATING) Ex: U.S. Report (Doc 4) Says it was militarily justified – COMPARE ACROSS DOCUMENTS: But the map shows that railroads were not hit… – Analyze: this means that… • If you can do this…you will be in a better spot than most juniors! Germans vs. “partisans” - punishing individuals - collective reprisals: entire villages slaughtered German soldiers shoot villagers in Yugoslavia, April 1941 Heaps of German soldiers at Stalingrad (240,000 German soldiers died) Operation Mincemeat and Fortitude • Proposed by Ian Fleming • Plan: Dress a body as a British spy, filled with misinformation Operation Fortitude: -Inflatable tank armies - Mass misinformation campaigns Terror bombing • Attacks on civilians a hallmark of Axis powers – Rape of Nanking – John Rabe • But Allies consider it too! • Terror bombing: – Night time bombing vs. Day time bombing • Incendiary vs. “High Explosive” – Dresden Second Front • Since Barbarossa, Stalin had begged for a 2nd Front • Britain and U.S. agree – Mix of noble and selfish reasons – “Fortress Europe” Strategic Differences • US: direct cross channel invasion of Nazi-held France • Britain: indirect approach, attacking through the “soft underbelly of Europe” • Noble and selfish reasons! – – – – Casualties Communism Protecting empire Postwar world British Approach American Approach What They Agreed On • Keep going and attack the “soft underbelly” – Tie down German soldiers in the South – British and Americans know this would mean no “2nd Front” in Europe until 1944 – But still prepare to invade rest of Europe – If you were a Soviet leader, what would you think…? – Set for May, 1944 • “Unconditional surrender” of Axis Powers Invasion of Italy • • • • July 1943, Americans and British Invaded Sicily. Next they invaded the Italian peninsula. Italians revolted against Mussolini and signed an armistice. But Germans in Italy kept up the fight. Germans didn’t surrender in Italy until May 2, 1945 . The Allied invasion of Italy diverted German resources from other places. • But if you’re the Soviet Union? IV. Operation Overlord - the DDay invasion June 6, 1944. Central Argument: With Germany’s defeat, superpower rivalries begin to emerge-defining the next 50 years to come. Yalta Conference • By February 1945, it was clear the Allies would win the war in Europe – – – – June 1944: D-Day Landing Allied air superiority Bombing campaigns in Germany proper Soviet Union chasing German armies • Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin met at Yalta to decide how to deal with Germany, how to rebuild Europe and how to win the war with Japan The View from the Soviet Union • 1941-1944: “Fighting alone” – Perception of allies • IMAGINE: If you were a Soviet citizen…what would you think about the allies? • Motivation for “Race to Berlin” • Additional U.S. campaigns: Market Garden, Battle of the Bulge Yalta Tensions • Roosevelt and Churchill wanted free elections in Eastern Europe • Roosevelt wanted Stalin’s support for the war against Japan and for the creation of the United Nations • Stalin wanted Germany weak, divided and controlled by the Allies But wait…who are the “Allies?” • Eventually 40+ nations – United in opposition to Germany, Japan, Italy • All pledge to follow the principles laid out in the ATLANTIC CHARTER – Document drafted by Britain and the U.S. • Seeds sown for union + disunion Yalta Compromises • Roosevelt and Churchill agreed Germany could be temporarily divided into four zones (American, French, British and Soviet) • Stalin agreed to “free and unfettered elections” in Eastern Europe, – Would join the war against Japan – Would support the creation of United Nations So… • When the United States and Britain hear that the Soviet Union is racing to Berlin, the question for U.S. generals is: • Race to Berlin as well? • Or secure Southern Germany, prevent Nazi leadership from escaping to Bavarian mountains? Timeline • • • • June 1944: D-Day landing November-December 1944: Battle of the Bulge April 1945: Race to Berlin May 1945: Battle and Fall of Berlin Race to Berlin • Stalin orders a “competition” between his best generals • Also knowledge: U.S. + Britain crossing the Rhine river into Germany too • Soviet Army: 2.5 million soldiers, 6000 tanks, 40,000 artillery pieces • Wehrmacht: 300,000 • Fear of Soviet retribution: 23 million Soviet dead The cost of the race • Incredible casualties • “Of our unit's 360 handsome young men who gathered at the Dnieper River, only 6 made it to Berlin” says one Soviet veteran. Berlin falls • • • • 90,000 old people and kids vs. Soviet army 1st wave of Soviet soldiers: highly disciplined 2nd wave: …not so much But why such a race for Berlin? • Operation Borodino: Soviet nuke program! • 3 tons of uranium recovered German bombings: Rotterdam, Coventry, London (and many, many more) Allied fire-bombing: many cities, including Dresden (Feb. 1945) VI The End of War in Europe • • • By April 1945 Russian troops from the East greeted their “Amerikanskie tovarishchi” (American comrades) from the West at the Elbe River in Germany. By the end of April the Russians captured Berlin. Hitler quickly married Eva and on April 30, 1945 they committed suicide. On May 7 Germany surrendered, and Allies proclaimed VE Day on May 8, 1945. April 30, 1945 Adolf Hitler commits suicide