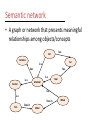
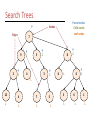
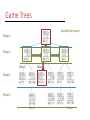
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AI Introduction
Technological singularity wikipedia , lookup
Personal knowledge base wikipedia , lookup
Visual Turing Test wikipedia , lookup
Turing test wikipedia , lookup
Knowledge representation and reasoning wikipedia , lookup
The Talos Principle wikipedia , lookup
Wizard of Oz experiment wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Computer Go wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Artificial intelligence in video games wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Artificial Intelligence CS105 Group Presentation Project • Week of November 7 to November 11 • Group presentation • Groups of 3/4 – – – – Each group will get 12/16 minutes maximum Each member must speak for 4 minutes Q&A session for 3/4 minutes Team Leaders • Topics: 1. An existing AI application(s) 2. An AI application that will possibly be created in the future and you would invest money in it 3. Technology in an AI movie – their advantages & disadvantages • Questions: What is it? How does it work? – Don’t have to explain any technical details if you don’t want to Group Presentation Project • Evaluation: – – – – Content and details Organization Member evaluation form Dress up on the day of presentation • Powerpoint files should be received BEFORE the beginning of class. • Attendance is mandatory this week Finding your group! Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence • Study and design of machines that can think like a human being – Attempt to understand human intelligence • But how do you define intelligence? – Abstract thought, understanding, communication, reasoning and learning, planning and problem solving • Goal: understand primary issues involved and the challenges Artificial Intelligence • Intelligent machines List 250099221 675490823 945784675 232343987 121108908 232308738 686532900 124345072 212576899 . . Turing Test • A behavioral test to determine whether a computer system is intelligent • Natural language processing • Knowledge about various topics • Reasoning Weak equivalence: The equality of two systems based on their results Strong equivalence: The equality of two systems based on their results and the process by which they arrive at those results State of the art Deep Blue beat Gary Kasparov, world champion in 1997 in a set of six games by two wins Search engines Tartan Racing: 2007 DARPA Urban challenge winner. Autonomous vehicle capable of driving in traffic. Mobile humanoid robots: MIT media labs Responsive environments: Bill Gates home TD Gammon learned how to play backgammon Foundations of AI • Psychology – How do humans and animals think and act? • Computer Science/Engineering – How to build an efficient computer system? • Linguistics – How does language relate to thought? • • • • • Philosophy Mathematics Economics Neuroscience Education / Learning Knowledge Representation • Many ways – Natural language : not efficient for processing – Mathematical notation: rigorous – Want: Logical view so we can process it efficiently • Capture facts and relationships Semantic network • A graph or network that presents meaningful relationships among objects/concepts has Cat Vertebra Fur is a has is a Animal has is a Mammal Bear is a is a lives in Fish lives in Water Whale Search Trees • Hierarchical structures that represents the alternatives of situations/choices – Nodes: Points in a tree that contains some form of data – Edges: Link between nodes in a search tree – Game tree: is a graph whose nodes are the positions in a game and whose edges are moves Search Trees P Edges Nodes 7 9 2 Parent nodes Child nodes Leaf nodes P C P C 5 4 P C 8 3 P C 6 P C L 0 P C L 12 4 7 L L L 3 5 L L 6 1 L L Game Trees Depth first Breadth first search search Player 1 Player 2 Wins! Wins! Player 1 Player 2 Wins! Wins! Thought Question Think of five questions that you might issue as the interrogator of a Turing test. Why would a computer have difficulty answering them well? Please explain your reasoning.