* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Global Versus Localized Marketing - Cal State LA
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
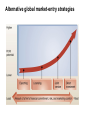
Global Versus Localized Marketing • Global marketing emphasizes selling the same product with the same marketing mix all over the world • Localized marketing emphasizes a unique marketing mix for each country or trading block Successful Global Marketing Requires: Comparative Advantage Opportunity THE LAW OF COMPARATIVE ADVANTAGE “Countries are better off producing items where they have inherent advantages and buying from others’ products where they have handicaps.” Foreign Market Selection Factors • Size of Market (enough customers?) • Distinct competitive advantage? • Level of Financial Risk – Cultural differences – Government instabilities Market Entry Strategies • • • • Export Licensing Joint ventures Investing in your own facilities Increasing levels of commitment, risk, control, and profit potential Risks in Global Marketing Trade Restrictions Currency Exchange Unstable Governments Cultural Factors Problems with Global Marketing can be due to: • Insufficient research on the intended countries • Overstandardization or lack of flexibility in approaches utilized Risks of Cultural Factors Standard of Living Differences Style of Living Differences Religion Differences Understanding Cultural Factors • Overseas buyers often have different concepts of time, space, and etiquette • Need to study how potential customers regard and use your product • Examples: – Privacy may be viewed differently – comparative advertising or sexual innuendo may be taboo Think Global But Act Local • • • • Global marketing often works and can save money Have global objectives But don’t ignore local market conditions Adjust plans to meet the special needs of particular customers in other countries DYNAMICS OF WORLD TRADE • A New Reality: Global Competition Among Global Companies for Global Customers Global Competition Global Companies • International Firm • Multinational Firm Multidomestic Marketing Strategy • Transnational Firm Global Marketing Strategy Concept Check 1. Cross-cultural analysis involves the study of _________. A: similarities and differences among consumers in two or more nations or societies Concept Check 2. When foreign currencies can buy more U.S. dollars, are U.S. products more or less expensive for a foreign consumer? A: Less expensive. Slide 7-32 GLOBAL MARKET-ENTRY STRATEGIES • Exporting Indirect Exporting Direct Exporting • Licensing Franchising • Joint Venture • Direct Investment Alternative global market-entry strategies Global Competition Global competition exists when firms originate, produce, and market their products and services worldwide. Multi-domestic Marketing Strategy Multinational firms use a multi-domestic marketing strategy when they have as many different product variations, brand names, and advertising programs as countries in which they do business. Global Marketing Strategy Transnational firms employ a global marketing strategy, which is the practice of standardizing marketing activities when there are cultural similarities and adapting them when cultures differ. Global Consumers Global consumers consist of customer groups living in many different countries who have similar needs or seek similar features and benefits from products or services. Cross-Cultural Analysis Cross-cultural analysis involves the study of similarities and differences among consumers in two or more nations or societies. Exporting Exporting is producing goods in one country and selling them in another country. Joint Venture A joint venture is when a foreign country and a local firm invest together to create a local business. Direct Investment Direct investment entails a domestic firm actually investing in and owning a foreign subsidiary or division.