* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C1&C2
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
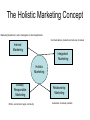
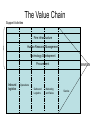
Understanding Marketing Management Professor Charles Trappey September 13, 2007 Defining Marketing for the 21st Century • Marketing is everywhere • Good marketing is an increasingly vital ingredient for business success • How might Samsung use a focus group to design a new mobile phone? The Importance of Marketing • Many companies now have CMO’s • But marketing is tricky and the C-level job holders can bring either great fortune or great disaster to the company. Can you think of an example, of a famous or infamous marketing person? The Scope of Marketing • Marketing deals with identifying and meeting human and social needs. • A shorter definition is “meeting needs profitably.” Frequently Asked Questions 1. How can we spot and choose the right marketing segments? McDonalds 2. How can we differentiate our offerings? Sogo 3. How should we respond to customers who buy on price? Traditional market 4. How can we compete against lower-price, lower-cost competitors? TSMC FAQ’s Continued 5. How far can we go in customizing our offering for each customer? Ford 6. How can we grow our business? Start-up 7. How can we build stronger brands? Acer 8. How can we reduce the cost of customer acquisition? Fed-Ex 9. How can we keep our customers loyal for longer? China Air Exchange and Transactions • Exchange is the core concept of marketing where a desired product is obtained from someone by offering something in return. • Self-produce, beg, steal, or eschange • A transaction is a trade of values between two or more partiers: A gives X to B abd receives Y in return. • In a transfer, A gives X to B but does not receive anything tangible in return. What is Marketed? • • • • • • • • • • Goods Services Events Experiences Persons Places Properties Organizations Information Ideas – every market offering includes a basic idea Key Customer Markets • • • • Consumer Markets Business Markets Global Markets Nonprofit and Governmental Markets Who Markets? • Marketers and prospects • Marketers seek to influence the level, timing, and composition of demand to met the organization’s objectives. There are 8 demand states: • Negative demand, non-existent demand, latent demand, declining demand, irregular demand, full demand, overfull demand, and unwholesome demand. New Consumer Capabilities • Substantial increase in buying power • Greater variety of goods and services • A great amount of information about practically anything • A greater ease in interacting and placing and receiving orders • An ability to compare notes on products and services How Business and Marketing are Changing • • • • • • • • • Changing technology Globalization Deregulation Privatization Customization Heightened competition Industry convergence Retail transformation Disintermediation and reintermediation (brick and click) Ten Rules of Radical Marketing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. The CEO must own the marketing function The marketing department must be small and flat and stay that way. Get face to face with the people that matter the most – the customer. Use market research cautiously. Hire passionate missionaries not marketers. Love and respect customers as individuals and not numbers on a spreadsheet. Create a community of consumers. Rethink the marketing mix. Celebrate common sense and compete with the larger competitors with fresh and different marketing ideas. Be true to the brand. Company Orientation Toward the Marketplace • The Production Concept – consumers want inexpensive and widely available products • The Product Concept – consumers want quality, performance and innovative features. • The Selling Concept – Customers will ordinarily not buy enough of the organizations products so therefore the company must undertake an aggressive sales and promotion effort. • The Marketing Concept – customer centered sense and respond. Selling focuses on the needs of the seller, marketing on the needs of the buyer. • Holistic Marketing is based on the development, design, and implementation of marketing programs, processes, and activities. The Holistic Marketing Concept Marketing Department, senior management, other departments Communications, products and services, channels Internal Marketing Integrated Marketing Holistic Marketing Socially Responsible Marketing Ethics, environment, legal, community Relationship Marketing Customers, channels, partners Core Concepts • Four P’s: – Product, Price, Place, Promotion • Four C’s: – Customer solution, Customer cost, Convenience, Communication • Needs, wants, demands Shifts in Marketing Management • From marketing does the marketing to everybody does the marketing • From organizing by product units to organizing by customer segments • From making everything to buying more goods and services from outside • From using many suppliers to working with fewer suppliers in a partnership Marketing Management Tasks • • • • • • • • Developing marketing strategies and plans Capturing marketing insights Connecting with the customers Building strong brands Shaping the market offerings Delivering value Communicating value Creating long term growth. Chapter 2 Marketing Strategy And Plans Marketing and Customer Value The Value Delivery Process • Choose the value (strategic marketing) – Customer segmentation, market selection/focus, value positioning • Provide the value (tactical marketing) – Product development, service development, pricing, sourcing, making, distribution and servicing • Communicate the value (tactical marketing) – Sales force, sales promotion, advertsing The Value Chain Support Activities Firm infrastructure Human Resource Management Technology Development Procurement Inbound logistics MARGIN Operations Outbound Logistics Marketing and Sales Service Core Competencies • It is a source of competitive advantage and makes a significant contribution to perceived customer benefits • It has applications in a wide variety of markets • It is difficult or competitors to immitate • Nike doesn’t make shoes, they have core competencies in shoe design and shoe merchandising Holistic Marketing and Customer Value • Value exploration – how can a company identify new value opportunities? • Value creation – how can a company efficiently create more promising new value offerings? • Value delivery – How can a company use its capabilities and infrastructure to deliver the new value offerings more efficiently? The Central Role of Strategic Planning • Planning – Corporate planning, division planning, business planning, product planning • Implementing – Organizing, implementing • Controlling – Measuring results, Diagnosing results, Taking corrective action Corporate and Division Strategic Planning 1. 2. 3. 4. Defining the corporate mission Establishing strategic business units Assigning resources to each SBU Accessing growth opportunities Defining the Corporate Mission • Mission statements are at their best when they reflect a vision for the next 20 years. • Focus on a limited number of goals • Stress the companies major policies and values • Define the major competitive spheres within which the company will operate Defining the Business • Market definitions of a business are superior to product definitions. • Levitt also says to define your business in terms of needs, not products. Assessing Growth Opportunities Organization and Organizational Culture Business Unit Strategic Planning The Business Mission SWOT Analysis Goal Formulation Strategic Formulation Program Formulation and Implementation Feedback and Control Contents of the Marketing Plan • Please carefully study the Sample Marketing Plan