* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Market Development Costs - McGraw Hill Higher Education
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
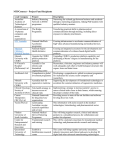
Chapter 5 Financing the International Operation Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-1 Chapter Learning Objectives • The various factors that create the need for increased capital. • What market entry and market development costs are. • The various sources of funding and support available to support the international marketing involvement. • The methods of international payment for goods. • The types of potential risks existing in international marketing involvement and the management of those risks. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-2 Global Perspective Exporting Risk: Global Implications of the Securitisation of US Housing Debt • Problems with global capital markets that first surfaced in the US have spread widely throughout the financial world. • Regulatory regime governing the global capital market has lagged behind economic growth, leaving investors and the global economy vulnerable to potential economic disaster. • The use of asset securitisation, the fastest growing sector of credit markets, has proliferated internationally and plays a vital role in the flow of global capital. • Political decisions and the resulting financial outcomes can unsettle the market environment. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-3 Global Perspective Exporting Risk: Global Implications of the Securitisation of US Housing Debt (cont.) • This environmental, political and financial volatility can be experienced as a global phenomenon or as an individual country market specific. • The wider the international operation, the greater the potential for high financial risks to arise. • Changes in the financial environment can influence: – The value of a country’s currency – The motivation to invest in a market – The market growth potential – Long-term expectations for the international marketer. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-4 Increased Need for Working Capital • Need for additional funds is relevant to the growth of the business internationally. • The potential risks associated with international marketing relate to: – Time it takes to prepare products and physically move them across borders. – Logistical characteristics of the host country. – Status of the infrastructure. – Changes in tariff and non-tariff structure. – Taxes imposed by home and/or host country. – Restrictions imposed on exchange transactions. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-5 Market Entry Costs • Preliminary research. • Specific research relating to specific industry and market conditions. • Selection and training of distributors. • Market visits: – Time – Opportunity costs – Travel costs • Other costs: – Legal fees – Site location and office set-up – licenses Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-6 Inventory • Three broad categories of costs: – Costs of manufacturing, warehousing and distribution. – Costs associated with physical facilities. – Costs of recruiting and training warehouse personnel. • Cost escalations and stock shortages associated with inventory management not only results in increased cash outlays but also loss of market share and longerterm loss of confidence. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-7 Market Development Costs • Market development activities focus primarily on integrated marketing communication efforts. • Other push strategy initiatives, or additional incentives, need to be included in the channel of distribution’s terms of trade. • The more substantial the stock – in terms of value, space requirements, maintenance, insurance and merchandising requirements – the more substantial the support needed. • In situations where channel control is critical for managing the business, companies may choose to acquire ownership of the channel. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-8 Capital Investment • Host country regulations may require a prescribed level of local content. • Marketers attempting to do business with economic blocs may have an advantage by conceding to local content rules. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-9 Sources of Funds • Commercial banks: – Largest source of funds for exporters. – Offer long- and short-term trade finance. – Key services include: Managing financing of international trade. Managing risks associated with importing and exporting. Managing payments for imports and exports. • Factoring and forfaiting • Government assistance: – EFIC – AusIndustry – Cooperative Innovation Program Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-10 A Comparison of the Characteristics of Factoring and Forfaiting Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-11 Australia’s Export Market Development Grants Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-12 Managing Financial Risks • Consideration of risks is important before entering into a contract of sale and in providing for the conduct of international marketing. • Key areas of risk include: – – – – – – – Political risk Exchange risk Shipping Custom clearance delays Quarantines Local legal conditions Standards regulations Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-13 Managing Financial Risks (cont.) • Strategies with respect to risk include: – Assessing the type, severity or likelihood of it occurring. – Pre-empting measures that can be adopted to avoid or minimise. – Actions available to the company to combat the effects of risk that does occur. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-14 Summary • • • • • One of the major concerns is the large commitment in new categories of cost beyond the local market costs. The need for increased working capital for procurement and inventory, market entry, market establishment and market maintenance costs must be considered. Involvement with international marketing and benefiting from the opportunities it offers present challenges as well as risks. Political risks may result from regime changes and/or change of government. These changes may bring about fundamental changes in the economic management of the country and create corporate ownership, operating and transfer risks for the foreign operator. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-15 Summary (cont.) • Commercial risks may include payment risks, insolvency, delivery risks, incovertibility of local currency and foreign exchange fluctuations. • Detailed risk management plan must be prepared based on a realistic assessment of the inherent risks existing in the country of interest. • Options available to deal with risks and effective and pre-emptive measures should be put in place. Copyright 2009 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a International Marketing by Cateora Slides prepared by Kate Mizerski, Edith Cowan University 5-16