* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing of High-Technology Products and Innovations Jakki J. Mohr
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
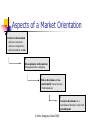
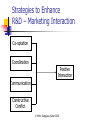
Marketing of High-Technology Products and Innovations Chapter 4: Market Orientation and R&D/ Marketing Interaction in High-Technology Firms Chapter Outline Market Orientation What it means to be Market Oriented Knowledge Management Facilitators of and Barriers to Being Market Oriented The Hidden Downside of a Market Orientation Marketing/R&D Interaction Relative to Innovation Type Barriers to Effective Interaction Strategies for Achieving Effective Interaction Keeping the Customer in Marketing/R&D Interaction © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Market Orientation What is a market orientation? What would you expect a market-oriented firm to look like? What are some advantages and disadvantages to being market-oriented? What are some advantages and disadvantages to being customer-focused vs. competitor-driven? What constitutes a knowledge management system? © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Market Orientation Philosophy of doing business that emphasizes shared gathering, dissemination, and utilization of market information in decision making. Impact of market orientation on performance: Firms that are strong technologically see a greater impact of market orientation on performance (than firms which are not strong technologically) © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Aspects of a Market Orientation 1 Gathers information -About customers -About competitors -About market trends 2 Disseminates information throughout the company 3 Makes decisions crossfunctionally based on use of information 4 Executes decisions in a coordinated manner and with commitment © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 How market-oriented firms use information: Gather information Disseminate information Across functions and divisions Utilize information Current and future customers Competitive information Market trends Across functions and divisions to enhance commitment Execute decisions in coordinated fashion © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Capturing Value from Knowledge Assets “The essence of the firm is its ability to create, transfer, assemble, integrate, and exploit knowledge assets.” David Teece © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Knowledge Management Proactive management of firm’s bases of knowledge to better share and use information Requires conscious oversight to overcome natural boundaries (between functions/divisions) © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 From Data to Knowledge Knowledge Information that enables prediction. Information Organized data. purpose & Data meaning Facts determined from a measurement of some kind. Scaling & accuracy © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Applicability & exploitability Influences on Achieving a Market Orientation Barriers Turf Protection Facilitating Conditions Core Rigidities Top Management Leadership Served Market Decentralized Responsibility Results Innovativeness Market Orientation New Product Success Superior Profitability Market-based Rewards © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Barriers to Being Market-Oriented People hoard information (selective behavior in the gathering and dissemination process) Core rigidities can cause people to disparage/disregard information about/from users (technology enthusiasm/arrogance) Tyranny of the served market: Listening only to current customers (marketing myopia) Users’ inability to envision new solutions Solving problems only with current technologies © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 The Hidden Downside to Being Market-Oriented Listening too closely to customers can inhibit innovativeness Customers may be inaccurate both in their positive endorsement of new products as well as in their rejection of new ideas. feedback fanatic syndrome © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Overcoming the Pitfalls in Being Market-Oriented Focus less on what customers SAY and more on what they DO. Empathic design Match use of customer feedback to the type of innovation: For incremental innovations: Customer feedback is vital and useful. For breakthrough innovations: Customers bounded by current solutions, and insights about new technologies may be sketchy at best. © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Overcoming the Pitfalls in Being Market-Oriented (Cont.) Focus on future customers (and not just existing customers) (investigate the possible causes of unexpected failure/success) Champion new ideas Work in cross-functional teams © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Customer-Led and Market-Oriented: Don’t Confuse the Two Customer-Led Expressed Wants Served Market Customer Satisfaction Linear Learning Customer Surveys Key Accounts Concept Testing Market-Oriented Unarticulated Needs New Customers Customer Value Breakthrough Learning Customer Observation Lead-Users Experimentation © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Effective Marketing/R&D Interaction nature of 1 Match interaction to the type of innovation 2 Examine and overcome core rigidity of elevation of engineering over marketing 3 Use formal and informal interactions to build bridges 4 Enhance opportunities for communication © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Nature of Marketing/R&D Interaction Matched to Type of Innovation Break-through innovations Success based on technological (R&D) prowess Role of marketing: To provide market-related feedback on market opportunity areas, market development, feedback on product features/engineering feasibility Marketing brings voice of customer and marketplace into the development process © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Nature of Marketing/R&D Interaction Matched to Type of Innovation (Cont.) Incremental Innovations Because customers can provide useful feedback for product development, role of marketing is critical Role of R&D: Ensure marketing understands technological capabilities Assist with marketing efforts Assist with understanding customers R&D remains “close to the customer” © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Barriers to R&D/Marketing Interaction Corporate culture/core rigidity that is technology-driven Elevates status of engineering over marketing personnel Engineering takes on important marketing tasks Spatial distance in physical locations of marketing and R&D Justifies and institutionalizes disregard for marketrelated information/feedback © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 R&D and Marketing Stereotypes R&D Marketing Time Orientation Long Short Projects Preferred Breakthrough Incremental Ambiguity Tolerance Low High Department Structure Informal Moderately Formal Bureaucratic Orientation Less More Primary Loyalty Profession Firm Professional Orientation Science Customer © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Strategies to Enhance R&D – Marketing Interaction Co-optation Coordination Positive Interaction Communication Constructive Conflict © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Co-optation. Effective marketers: Build informal networks and bridges to engineering Give the credibility to those who understand products, technology, markets and be able to communicate articulately about the other’s domain Form strategic coalitions with upper management Risk: May alienate peers If necessary, bypass engineering to get the job done via external partners (a way of governance) © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Cooperative Strategies Co-locate marketing and R&D in close proximity Rotate personnel through different functions Develop cross-functional networks Create group incentives that encourage cooperation Build consensus in a nondirective fashion © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Communication Increased frequency of communication beyond minimum threshold (125/3-month), but below overload (525/3-month) Disseminate information through formal channels when possible for credibility Create norms for extensive sharing of information between functions Make it clear that the organization’s goals are subordinate to either marketing’s or R&D’s individual goals © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Constructive Conflict Spirited discussion creates new and innovative ideas Pressure for harmony stifles emergence of alternative viewpoints Result of emphasis on harmony may be “groupthink” where contrary opinions are not expressed and problems are ignored Key to “constructive” conflict is respect Once a decision is made, no second guessing! © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Caveat: Effective marketing/R&D interaction must be firmly grounded in an understanding of customer needs and wants. © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 Keeping the Customer In R&D/Marketing Interaction? Customer Sure Marketing Engineering Product Technology Rock Pile Would you like a rock? Find me a big, cheap, fast, dense, OK sharp...rock Here’s a Wrong blue rock? rock Do you have a red rock? OK, but only if its square What’s wrong with blue? I can make a purple one We don’t have square ones © Mohr, Sengupta, Slater 2005 …