* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the PowerPoints
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Brand loyalty wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Brand ambassador wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Emotional branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
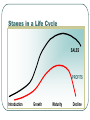
Develop a New Product Marketing Chapter 10 What is a Product Anything tangible offered to a market by businesses to satisfy needs Products are more than an item • Businesses need to consider consumer wants and needs Consumers know best Businesses believe they know what the consumers need • Big mistake Consumers will show businesses what they want/need with what they will buy Product Development What is the failure rate of new products? Why…. • 50% • Products do not meet consumer needs or are not superior to competing products The Role of Marketing Gather information • Marketing research Designing Strategies • • • • Identifying target markets Determining company strengths Evaluating market positions Suggesting alternative marketing mixes Testing Marketing Mixes • • Focus groups Consumer Panels Designing a Product Basic Product • • Most important part of product Simplest form of product Enhanced Product • Features and options added to basic product to meet several consumer needs Extended Product • • Services, guarantees, information on effective use of the product Even additional products that improve the use of the product Positioning for Competitive Advantage Market Position • Unique image of a product in a consumer’s mind Bases for Positioning Attribute Price and Quality • Highlighting a product feature • May indicate a high price as a sign of quality or low price as a sign of value Use or Application • Stressing a unique use or application for a product Bases for Positioning Product User • encourages use of a product or service by associating a personality or type of user with the product Product Classification • Associate the product with a particular category of products Competitor • Demonstrating how they are against the competition Warm-Up Why does developing even a simple product like a toothbrush involve so many decisions? Product Mix Components Product Line • Group of similar products with slight variations • in the marketing mix to satisfy different needs in a market. Variation in Quantity • Different package size or quantity • Variation in Quality • Adding features to the basic product Product Mix Components Assortments • Complete set of all products a business offers to its market Packaging Serves as a dual purpose Improves product • Protection and promotion • Example: pour spouts, resealable liners Packaging Ease of Use • Must carefully consider how a consumer will use the product Safety • Safety and protection important concerns, • especially when product is used by children Fragile products need packaging to protect during display and shipping Packaging Attraction • Conveying a certain image • Attracting a buyer based on the enticing package Handling • Display and security Packaging Environment • Type and quantity of materials used Brand Development Brand • Name, symbol, word, or design that identifies a product Trademark • Legal protection of the words or symbols used by one company Brand Development Licensed Brand • Well known name or symbol established by one company and sold for use by another company to promote its products Brand Development Levels of Brand Recognition • Non recognition • Unable to identify brand • Rejection • Will not purchase because of the brand • Recognition • Recall the brand; little influence Brand Development Levels of Brand Recognition • Preference • View brand as valuable and choose it if available • Insistence • Reject other brands Selecting Target Markets A target market is a clearly identified segment of the market to which the company wants to appeal. Buying Motives Reasons you buy: • Emotional motives Based on feelings, beliefs or attitudes • Rational motives Based on facts or logic • Patronage motives Based on loyalty Influences on Decision Making Personality Social Class • Well defined enduring pattern of behavior • Lifestyle, values and beliefs common to a group of people Influences on Decision Making Cultural Environment • Set of beliefs or attitudes that are passed on from one generation to another Reference Groups • Organizations from which you take your values and attitudes Types of Decision Making Routine Decision-Making • Purchases made frequently and do not require much thought Limited Decision-Making • Takes more time and is often used with more expensive products or products purchased less frequently Types of Decision Making Extensive Decision-Making • Goes through all five steps of the decision making process Types of Competition Direct • competition in a market segment with businesses that offer the same type of product or service Indirect • when a business competes with a product that is outside its classification group Selecting Target Markets A target market is a clearly identified segment of the market to which the company wants to appeal. Types of Competition Price Competition • rivalry among businesses based on price and value Non-Price Competition • focuses on non price factors of its product such as quality, location, service, etc. Using Life Cycle Analysis Three factors to consider when planning a marketing mix: the type of competition the purchase behavior of consumers the strengths and weaknesses of the business Stages in a Life Cycle SALES PROFITS Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Stages of a Product Life Cycle Introduction First Stage; little or no competition Basic product; Higher prices; promotions to target market; widely distributed Growth Sales are growing; competition emerges New features; more distribution (wholesalers/retailers); range of prices (emphasize value); more money spent on promotion Stages of a Product Life Cycle Maturity Sales peak and profit begins to decline Intense competition; Growth Sales are growing; competition emerges New features; more distribution (wholesalers/retailers); range of prices (emphasize value); more money spent on promotion Purchase Classifications Convenience Goods • Staple goods • Products you buy that are regular routine purchases • Impulse Goods • Purchase on spur of the moment with out advance planning • Emergency Goods • Products purchased as a result of an urgent need Purchase Classifications Shopping Goods • Attribute-based goods • Consumers see a number of factors to determine best value • Basing purchase on many things such as features, service, price, use of credit • Price-based goods • Consumers see products basically alike • Basing purchase on price Product Classification Specialty Goods • Consumers will not substitute or buy product from any other business or brand • Strong brand loyalty • Not just expensive items, but items you regularly buy… • Factors determining specialty goods • Importance in satisfying need • Willingness of customer to delay purchase until specific product/brand is located Product Classification Unsought Goods • Products consumers do not want to buy