* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Consumer Behavior: People in the Marketplace
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 1
Marketing: Managing
Profitable Customer
Relationships
PowerPoint by
Kotler & Armstrong
(and modified by me)
1-1
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Chapter Big Ideas
The Big Ideas in this chapter are:
Marketing is….
Major concepts and tools of marketing
Market orientations
CRM
1-2
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing
So what’s Marketing?
Function: noun
Etymology: Middle English, from Old
North French, from Latin mercatus --trade or marketplace
1-3
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing
Marketing is the process of planning
and executing the conception, pricing,
promotion, and distribution of goods,
services and ideas to facilitate
satisfying exchange relationships with
customers in a dynamic environment.
(AMA)
1-4
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing
Marketing is the process of planning and
executing (Management function)
the conception, pricing, promotion, and
distribution (4 P’s)
of goods, services and ideas (Product)
to facilitate satisfying exchange
relationships (buying and selling)
with customers (Target/Segment)
in a dynamic environment. (External
factors)
1-5
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Factors
Influencing
Company
Marketing
The Four P’s
1-6
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Elements of a
Modern Marketing System
1-7
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Core Marketing Concepts
1-8
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing Concepts and Tools
Core Marketing Concepts
1. Target Markets and Segmentation
2. Marketers and Prospects
3. Needs, Wants, and Demands
1-9
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing Concepts and Tools
4. Product, Offering, and Brand
5. Value and Satisfaction
Value
Value = Benefits / Costs =
(Functional benefits + Emotional benefits) /
(Monetary costs + Time costs + Energy costs + Psychic
costs)
1-10
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing Concepts and Tools
6. Exchange and Transactions
7. Relationships and Networks
Relationship marketing
Marketing network
8. Marketing Channels
9. Supply Chain
10. Competition
Brand competition
Industry competition
Form competition
Generic competition
1-11
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing Concepts and Tools
11. Marketing Environment
12. Marketing Mix (4 P’s)
13. Marketing Program
1-12
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Management Orientations Toward
the Marketplace
Production
Concept
Product
Concept
Selling
Concept
Marketing
Concept
Societal
Marketing
Concept
1-13
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
CRM
CRM is what?
Customer relationship management (also
called CRM) is defined as:
“the overall process of building and
maintaining profitable customer
relationships by delivering superior
customer value and satisfaction.”
1-14
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
CRM
It costs 5 to 10 times MORE to attract a new
customer than it does to keep a current
customer satisfied.
Marketers must be concerned with the
lifetime value of the customer.
1-15
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing Challenges
Source of marketplace changes:
Technological advances
Rapid globalization
Continuing social and economic shifts
1-16
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Chapter 2
company and Marketing
Strategy: Partnering to
Build Customer
Relationships
PowerPoint by
Kotler & Armstrong
(and modified by me)
1-17
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Chapter 2 – Big Ideas
Strategic planning
Value creation (in many forms)
1-18
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Strategic Planning
Strategic Planning is?
The Process of Developing and
Maintaining a Strategic Fit
Between the Organization’s Goals
and Capabilities and Its Changing
Marketing Opportunities.
1-19
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
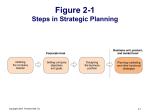
Steps in Strategic
Planning
1-20
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
The Mission Statement
What’s Mission Statement?
A statement of the organization’s purpose
What it wants to accomplish in the larger
environment
Should be market oriented and defined in
terms of customer needs.
1-21
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Questions a Mission Statement
Should Answer
What is our Business?
Who is the Customer?
What do Consumers Value?
What Should our Business Be?
1-22
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Mission Statements Should:
Be Realistic
Be Specific
Fit the Market Environment
Be Based on Distinctive Competencies
Be Motivating
1-23
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Designing the Business
Portfolio
A business portfolio is what?
The business portfolio is the collection of
businesses and products that make up the
company.
During the strategy process a company must
do what?
analyze its current business portfolio or Strategic
Business Units (SBUs),
decide which SBUs should receive more, less, or
no investment,
develop growth strategies for growth or
downsizing.
1-24
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Portfolio Analysis
A portfolio analysis is what?
An evaluation of the products and business
making up the company.
Resulting in?
Identifying where resources are directed or
taken away
Invest in to more profitable businesses and
Divest in weaker ones (phased down or dropped).
1-25
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Strategic Business Unit
A SBU is what? (hint: )
A unit of the company that has a separate
mission and objectives and that can be
planned independently from other company
businesses.
Can be a company division, a product line
within a division, or sometimes a single
product or brand.
1-26
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Strategic Planning Tools
BCG’s growth share matrix
Ansoff’s product/market expansion grid
1-27
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Analyzing Current SBU’s:
BCG Growth-Share Matrix
Relative Market Share
High
Low
Question Marks
Low
Market Growth Rate
High
Stars
• High growth & share
• May need heavy
investment to grow
• Eventually, growth will slow
Cash Cows
• Low growth, high share
• Established, successful
SBU’s
• Produce cash
?
• Low share SBUs in high growth
markets
• Require cash to hold
market share
• Build into Stars or phase out
Dogs
• Low growth & share
• Generate cash to sustain self
• Do not promise to be cash
sources
1-28
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Problems With Matrix
Approaches
Can be Difficult, Time Consuming, Costly to Implement
Difficult to Define SBUs & Measure Market Share/Growth
Focus on Current Businesses, Not Future Planning
Can Place too Much Emphasis on Growth
Can Lead to Poorly Planned Diversification
1-29
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Product/Market Expansion Grid
PRODUCT
MARKET
Existing
New
Existing
Market
Penetration
Product
Development
New
Market
Development
Diversification
1-30
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Value
Value is what?
Function: noun
Pronunciation: 'val-(")yü
Etymology: past participle of Latin
valEre – to be worth, be strong, be
powerful, be influential, be healthy
Meaning:
“Relative worth, utility, or importance”
1-31
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Value Proposition
Value Proposition is what?
A set of benefits offered by an
organization to satisfy a customer’s
needs, wants and demands
1-32
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Value Chain
So what’s a Value Chain?
A Michael Porter concept
A tool to conceptualize and identify ways to
create more customer value
9 Activities
5 primary activities
Inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics,
marketing and sales, service
4 support activities
Procurement, technology development, human resources,
firm infrastructure
1-33
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
The Generic Value Chain
1-34
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Value Delivery Network
So what’s a value delivery network?
A network made up of the company,
suppliers, distributors, and ultimately
customers who “partner” with each other
to improve the performance of the entire
system
1-35
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Value Delivery Network
Company’s Value Chain
Distributors
Suppliers
Customers
1-36
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Market Segmentation
So what’s market segmentation?
The process of dividing a market into
distinct groups of buyers with different
needs, characteristics, or behavior who might
require separate products of marketing
programs.
A market segment consists of consumers who
respond in a similar way to a given set of
marketing efforts.
1-37
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Target Marketing
So what’s target marketing?
Involves evaluating each market segment’s
attractiveness and selecting one or more
segments to enter or target.
Target segments that can sustain profitability.
1-38
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Market Positioning
Arranging for a product to occupy a clear,
distinctive, and desirable place relative to
competing products in the minds of target
consumers (e.g., Chevy Blazer: “Like a rock”)
Process begins with differentiating the company’s
marketing offer so it gives consumers more value.
1-39
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
The Marketing Mix
The set of
controllable,
tactical marketing
tools that the firm
blends to produce
the response it
wants in the
target market.
Consists of the 4 P’s
1.
2.
3.
4.
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
1-40
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
The 4 P’s of the Marketing Mix
1-41
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Managing the Marketing Effort
Strategic
Tactical
1-42
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Major Sections of Product/Brand
Plan
Executive Summary
Current Marketing Situation
Analysis of Threats and Opportunities
Objectives for the Brand
Marketing Strategy
Action Programs
Marketing Budget
Controls
1-43
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing Control
Process
1-44
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Marketing Concept
Value
Creation
1-45
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Value and Value Proposition
Value
The relative worth, utility or importance
Value
Value = Benefits / Costs =
(Functional benefits + Emotional benefits) /
(Monetary costs + Time costs + Energy costs + Psychic costs)
Value Proposition
A set of benefits offered by an organization to satisfy a
customer’s needs, wants and demands
1-46
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Value Chain
A tool to conceptualize and identify ways
to create more customer value
9 Activities
5 primary activities
Inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics,
marketing and sales, service
4 support activities
Procurement, technology development, human
resources, firm infrastructure
1-47
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
The Generic Value Chain
1-48
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Value Delivery Network
A network made up of the company,
suppliers, distributors, and ultimately
customers who “partner” with each other
to improve the performance of the entire
system
1-49
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Value Delivery Network
Company’s Value Chain
Distributors
Suppliers
Customers
1-50
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Market Segmentation
The process of dividing a market into
distinct groups of buyers with different
needs, characteristics, or behavior who
might require separate products of
marketing programs.
A market segment consists of consumers
who respond in a similar way to a given set
of marketing efforts.
1-51
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Target Marketing
So what’s target marketing?
Involves evaluating each market segment’s
attractiveness and selecting one or more
segments to enter.
Target segments that can sustain profitability.
1-52
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Market Positioning
Arranging for a product to occupy a clear,
distinctive, and desirable place relative to
competing products in the minds of target
consumers (e.g., Chevy Blazer: “Like a rock”)
Process begins with differentiating the company’s
marketing offer so it gives consumers more value.
1-53
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
The Marketing Mix
The set of
controllable,
tactical marketing
tools that the firm
blends to produce
the response it
wants in the
target market.
Consists of the 4 P’s
1.
2.
3.
4.
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
1-54
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.
The 4 P’s of the Marketing Mix
1-55
Copyright © 2003 Prentice-Hall, Inc.