* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Partnering to Build Customer Relationships
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
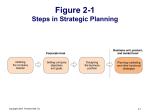
CHAPTER 2 Company and Marketing Strategy: Partnering to Build Customer Relationships Roadmap: Previewing the Concepts Explain companywide strategic planning and its four steps. Discuss how to design business portfolios and growth strategies. Explain marketing’s role in strategic planning and how marketing works with its partners to create and deliver customer value. Describe the elements of a customer-driven marketing strategy and mix, and the forces that influence it. List the marketing management functions, including the elements of a marketing plan. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-2 NIKE – Strategy: Then and Now Early Days Characterized by “seat of the pants” management. Innovative sneaker tread drove early success. Technological product superiority, big-name endorsements, and “Just Do It” ads revolutionized sport marketing. 1980s – 1990s: Nike leverages brand strength into new product areas. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. Late 1990s - Present Changes in consumer shoe preference, declining product innovation, and negative PR plague Nike. Anti-establishment image no longer works: brand backlash occurs. Strategic planning is embraced & Nike focuses on innovation & exploring new market opportunities. Nike has global success. 2-3 Strategic Planning The process of developing and maintaining a strategic fit between the organization’s goals and capabilities and its changing marketing opportunities. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-4 Figure 2-1 Steps in Strategic Planning Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-5 The Mission Statement A statement of the organization’s purpose. – What it wants to accomplish in the larger environment. Should be market oriented and defined in terms of customer needs. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-6 Market-Oriented Mission Statements Should address the following questions: – What is our business? – Who is our customer? – What do consumers value? – What should our business be? Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. Mission statement must also be: – Realistic. – Specific. – One that fits the market environment. – Based on distinctive competencies. – Motivating. 2-7 Let’s Talk! The mission statement now In 2002 Microsoft’s reads, "At Microsoft, we mission was "To work to help people and empower people businesses throughout the through great world realize their full software -- any potential.” time, any place, Evaluate and on any Microsoft’s new mission against device.” the criteria previously discussed. How does it fare? Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-8 Designing the Business Portfolio The business portfolio is the collection of businesses and products that make up the company. The company must: – Analyze its current business portfolio or Strategic Business Units (SBUs); – Decide which SBUs should receive more, less, or no investment; – Develop strategies for growth or downsizing. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-9 Strategic Business Unit (SBU) A unit of the company that has a separate mission and objectives and that can be planned independently from other company businesses. Can be a company division, a product line within a division, or sometimes a single product or brand. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-10 Marketing in Action Strategic Business Units The Symrise company creates ingredients used in flavors, fragrances, and cosmetics. The Flavors Division is structured into SBUs which are responsible for developing the product categories shown at left. http://www.symrise.com Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-11 Portfolio Analysis An evaluation of the products and business making up the company. Resources are directed to more profitable businesses and weaker ones are phased down or dropped. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-12 Figure 2-2 The BCG Growth-Share Matrix Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-13 Problems with Matrix Approaches Can be difficult, time consuming, and costly to implement. Difficult to define SBUs and measure market share and growth rate. Focus is on current businesses; gives little help with future planning. Can place too much emphasis on growth. Can lead to poorly planned diversification. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-14 Product/Market Expansion Grid Helps in the identification, evaluation, and selection of market growth opportunities. – Marketing must achieve profitable growth for the firm. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-15 Figure 2-3 The Product/Market Expansion Grid Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-16 Market Penetration Strategy: to increase sales to current buyers without changing the products being sold. Market penetration can be achieved by adding new stores in current market areas, improving advertising, lowering prices, adding services, etc. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-17 Market Development Strategy: identify and develop new markets – demographic or geographic – for current products. Bass Pro Shops has aggressively developed new geographic markets for its Outdoor World retail stores. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-18 Product Development Strategy: offering modified or new products to current markets. – How? Adding new sizes, flavors, or offerings, co-branding products, etc. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-19 Diversification Strategy: start up or buy businesses outside of current products and markets. – Diversification is the riskiest strategy. – Firms that diversify too broadly into unfamiliar products or industries can lose their market focus. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-20 Let’s Talk! Video Snippet After watching the Mayo Clinic video clip, answer the following questions: What growth strategies were used by the Mayo Clinic? Are there additional growth opportunities that could be pursued? Explain. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-21 Planning Marketing Marketing plays a key role in strategic planning: – Provides a guiding philosophy. The Marketing Concept – Provides input to strategic planners. – Designs strategies to reach objectives. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-22 Value Chain Each company department engages in some type of value-creating activity. – Purchasing – Marketing – Operations, etc. Coordination between departments is key to providing superior value. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-23 Value Delivery Network Components include: – Company’s value chain Each department is a link in the value chain. – Distributors Many groups contribute – Suppliers to Wal*Mart’s value chain – Customers Improved performance in delivery value to customers is the goal. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-24 Figure 2-4 Managing Marketing Strategy and the Marketing Mix Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-25 Market Segmentation The process of dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers with different needs, characteristics, or behavior who might require separate products or marketing programs. A market segment consists of consumers who respond in a similar way to a given set of marketing efforts. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-26 Target Marketing Involves evaluating each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more segments to enter. Target those segments that can sustain profitability. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-27 Marketing in Action Target Marketing Jones Soda caters to its niche of 12- to 24-yearolds who “appreciate the brand’s wacky and irrelevant attitude”. Loyal consumers help design product flavors, colors, labels, and brand names. Visit the Web site to learn more. www.jonessoda.com Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-28 Market Positioning Arranging for a product to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target consumers. Begins with differentiating the company’s marketing offer so it gives consumers more value. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-29 Marketing in Action Positioning Promoting attributes, benefits, usage situations, or users can help to establish a product’s position in the consumer’s mind. How is the Gelstat Migraine medicine being positioned? Is this ad effective? Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-30 The Marketing Mix The set of controllable, tactical marketing tools that the firm blends to produce the response it wants in the target market. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-31 Figure 2-5 The Four “Ps” of the Marketing Mix Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-32 The 4 Ps and the 4 Cs of the Marketing Mix 4 Ps – Seller’s View – Product – Price – Place – Promotion Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 4 Cs – Buyer’s View – Customer Solution – Customer Cost – Convenience – Communication 2-33 Let’s Talk! Select either ultimate consumers or businesses as your target market. Explain each element of Visa’s marketing mix – product, price, place, and promotion – in the context of marketing Visa towards your selected target market. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-34 Figure 2-6 Marketing Analysis, Implementation, Planning, and Control Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-35 Marketing Management Functions Analysis feeds the development of strategic plans. Division, product, and brand level plans are implemented. Marketing activities are evaluated and corrected as part of control process. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-36 Marketing Management: Analysis The SWOT analysis is critical: – Finding opportunities – Avoiding threats – Understanding strengths – Analyzing weaknesses Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-37 Figure 2-7 SWOT Analysis Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-38 Marketing Management: Planning Brand / Product Marketing Plan: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Executive summary Current marketing situation Analysis of threats and opportunities Objectives for the brand Marketing strategy Action programs Marketing budget Controls Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-39 Marketing Management: Implementation Plans are turned into action with day-to-day activities. Good implementation is a challenge. Marketing departments must be properly organized to ensure timely implementation. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-40 Marketing Department Organization Function Geography Product Geographic organization is very common for national and international marketers. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. management Market or customer Combination of two or more of the above 2-41 Let’s Talk! Under what circumstances does it make sense to structure the marketing department by combining a product management organizational system with a customer organizational system? Offer an example of a specific manufacturer for which you feel this would be appropriate. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-42 Marketing Control Process Set Goals Measure Performance Evaluate Performance – Operating Control – Strategic Control The marketing audit is major tool. Take Corrective Action Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-43 Figure 2-8 Return on Marketing Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-44 Rest Area: Reviewing the Concepts Explain companywide strategic planning and its four steps. Discuss how to design business portfolios and growth strategies. Explain marketing’s role in strategic planning and how marketing works with its partners to create and deliver customer value. Describe the elements of a customer-driven marketing strategy and mix, and the forces that influence it. List the marketing management functions, including the elements of a marketing plan. Copyright 2007, Prentice-Hall Inc. 2-45