* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Market
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Sports marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
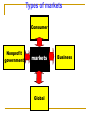
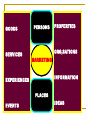
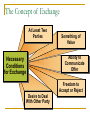
An Overview of Marketing 1 Course Instructor: Sean X.H. Qiu Lecturer, MDL 1 Learning Objectives 1..Why do we need to learn marketing? 2. What is a market and its types? 3. What is Marketing? 4. What is Marketed? 5. What is demand and its types? 6. What are some Core Marketing Concepts? 7. Describe Various marketing management philosophies? 1. Why do we need to learn Marketing ? Can you sell these products Easily ? How about these products? How about them ? Can you Market them? How about Their films ? Why Marketing for cooperatives and Coop Products ? Why Study Marketing? Plays an important role in society Vital to business survival, profits and growth Offers career opportunities Affects your life every day Why Study Marketing? “Marketing is too important to be left to the marketing department.” ---David Packard Hewlett-Packard Why Study Marketing? • Professional Selling Everything must be made as simple as possible but not one bit simpler --- Albert Einstein • Marketing Research Fastest route up the corporate ladder • Product Management • Advertising • Retail Buying • Distribution Management • Product Development • Wholesaling Why Study Marketing? Global economy: (PIII) International Trade & Domestic Trade One World, Many Wallets: Economic Conflicts, Culture Shock and Market Shock 2. What is Market and its types? What is a market? Market ( Market place) A physical place where buyers and sellers gather to exchange goods and services Types of markets Consumer Nonprofit government markets Global Business 1. Consumer Market Consists of all individuals or house holds who buy or acquire offerings for personal usage. 2. Industrial/Business Market Consists of buyers who purchase or acquire offerings for resell or reproduction to earn profit 3. Global Market/International markets. Import, export etc. 4. Non Profit & Government Markets 3.What is Marketing? What is Marketing? Personal Selling? Advertising? Making products available in stores? Maintaining inventories? All of the above, plus much more! What is Marketing? American Marketing Association Definition Marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals. Kotler’s Defination The Art & Science of choosing Kotler’smarkets defination : target and getting, keeping and growing customers through creating, delivering and communicating superior customer value Marketing VS Sales Process and Result (P.1) Sales occur when goods or services are “given over” to a customer in exchange for money or another valuable consideration. It’s the end of the marketing process. Marketing describes the whole commercial process that creates (through promotion) the interest that the potential customer demonstrates prior to a sale. 4.What is Marketed? GOODS SERVICES PERSONS PROPERTIES ORG,SATIONS MARKETING INFORMATION EXPERIENCES PLACES EVENTS IDEAS What is Marketed? Basically 10 types of entities are being marketed. Goods Consumer goods, industrial goods Services Intangible offerings of people or organizations Experiences Tourism, Recreation, adventure Events Anniversaries, shows, testimonials Persons Marketing one's self e.g. celebrities, politicians, artists etc. Places Cities, states, regions, historical places, tourism. Properties Intangible rights of ownership either real property (real estates) or financial property ( stocks & bonds). Organizations Firms, Universities, museums. Information News, views like encyclopedias news papers etc. Ideas New ideas/research about production, services, advertisement etc. You can market only if there is demand for them…… 5. What is Demand? NEGATIVE NO DEMAND LATENT DEMAND DEMAND STATES DECLINING DEMAND DEMAND STATES IRREGULAR DEMAND FULL DEMAND OVERFULL DEMAND Unwholesome demand 1. Negative Demand consumer dislike product and may even pay a price to avoid it. The marketing task is to analyze why the market dislike product and adopt the strategy to change the attitude of consumer. 2. No Demand consumer may be unaware or uninterested In product. The marketing task is to find ways to connect the benefits of the product with the person’s natural needs and interests. 3. Latent Demand Want of consumers exist but not marketing offer to satisfy need. The marketing task is to measure the size of potential market and develop good and services to satisfy that want. 4. Declining Demand Consumers begin to buy the product less frequently or not at all. Marketing task is to reverse declining demand through creative marketing. 5. Irregular demand Variations in demand on seasonal, daily or even hourly bases. The marketing task called Synchromarketing is to find the ways to alter the pattern of demand through flexible pricing, promotion and other incentives. 6. Full Demand supply= demand. The marketing task is to maintain the pattern of demand 7. Overfull Demand Demand level is high as compare to organizational production capacity. Marketing task is called demarketing is to find ways to reduce demand temporarily or permanently. 8. Unwholesome Demand Consumers may be attracted to products that have undesirable social consequences. The marketing task is to organize activities eg. Fear messages, price hikes or reduced availability. 6. What are some Core Marketing Concepts? The Concept of Exchange At Least Two Parties Necessary Conditions for Exchange Something of Value Ability to Communicate Offer Freedom to Accept or Reject Desire to Deal With Other Party Exchange involves obtaining a desired product from someone by offering something in return. A person can obtain a product by 4 ways Self Produce By Force Beg Exchange ( Core of Marketing ) Transfer A gives something to B but doesn’t receive anything tangible in return. Transaction A trade of values between two or more parties, involves at least two things of value, agreed-upon conditions, a time of agreement, and a place of agreement. Important Definitions Marketer is a some one who is seeking a response (attention, a purchase, a vote, a donation) from another party called prospect. Prospects means future potential buyer Need, Wants, and Demand Need Basic human requirement Want Need becomes want when it is directed to specific object that satisfies need. Demand want for specific product backed by purchasing power. Market ( Market place) A physical place where buyers and sellers gathered to exchange to exchange goods. Market Space exchange of goods without physical market (digital, Virtual) e.g. eCommerce, internet etc. Target Market People/place for whom seller designs his particular offering. Segmentation Division of market in small groups keeping on any base (Purchasing power, age, social values etc.) Metamarket refers to a cluster of complementary goods and services that are closely related in the minds of consumers but are spread across a diverse set of industries. Customer Value It is ratio between what consumer gets & what he gives Value = Benefits / Costs Total Customer value Customer Delivered Value Total Customer Cost Product value Monetary cost Service Value Time cost Personal value Energy cost Image value Psychic cost Customer Satisfaction The feeling that a product has met or exceeded the customer’s expectations. It’s related with how well the product performance lives up to customers expectation. Relationship Marketing Maintaining satisfying and long term relationship with customers, partners, suppliers and other channel members. Relationship Marketing’s Importance Attracting a new customer may be TEN TIMES the cost of keeping an old customer Effective Marketing: Binding the Buyer and Seller Remember: The binding relationship between the buyer and seller that’s created by effective marketing tends to last longer --- and to be set up more quickly --- as the speed of information in the marketplace increases. 7. What are Various Marketing philosophies? product Selling Competing Concepts Production MARKETING SOCIETAL MARKETING Marketing Management Philosophies Production Concept Product Concept Competing Philosophies Selling Concept Marketing Concept 1. Production Concept holds that consumers will prefer products that are widely available and inexpensive. Therefore, management should focus on improving production and distribution efficiency. Focused on high production efficiency, low cost and mass distribution. Useful in/if : competition is weak . Demand exceeds supply Developing countries, where customers are more interested in product rather then features. generic products competing on price narrowly Poor quality, no customer satisfaction, focused market. 2. Product Concept holds that consumers will favor products that offer the most in quality, performance, and innovative features. Thus, an organization should devote energy to make continuous product improvements. A General Motors executive said years ago: “ How can the public know what kind of car they want until they see what is available?” But A new or improved product will not necessarily be successful unless the product is priced, distributed, advertised and sold properly Product oriented companies often design products with no or very little consumer input. They give more importance to products rather then consumers. 3. The Selling Concept holds that consumers will not buy enough of the firm’s products unless it uses a large-scale selling and promotion effort. The concept is typically practiced with unsought goods those that buyers do not normally think of buying, such as insurance or blood donations, encyclopedias, fund-raisers, college admissions offices and by specially political parties etc. Coca-cola’s VP said “ The purpose of marketing is to sell more stuff to more people more often for more money in order to make more profit”. Their aim is to sell what they make rather than make what the market wants 4. The Marketing Concept holds that achieving organizational goals depends on knowing the needs and wants of target markets and delivering the desired satisfactions better than competitors do. Under the marketing concept, customer focus and value are the paths to sales and profits. Marketing concept is a customer-centered “sense and respond” philosophy. It views marketing not as “hunting,” but as “gardening.” The job is not to find the right customers for your product, but the right products for your customers The marketing concept starts with a well-defined market, focuses on customer needs, and integrates all the marketing activities that affect customers. In turn, it yields profits by creating long-term customer relationships based on customer value and satisfaction. 5. The Societal Marketing Concept holds that the organization should determine the needs, wants, and interests of target markets. It should then deliver superior value to customers in a way that maintains or improves the consumer’s and the society’s well-being. It questions whether the pure marketing concept overlooks possible conflicts between consumer short-run wants and long-run welfare of consumer and society. The fast food industry offers tasty but unhealthy food with high fats, salts starch. The products are wrapped in convenient packaging, but this leads to waste and pollution. Thus, in satisfying short-term consumer wants, the highly successful fast-food chains may be harming consumer health and causing environmental problems 6. Holistic Marketing Concept is based on development, design and implementation of marketing programs, processes and activities that recognizes their extent and interdependencies. It holds that “everything matters" in marketing and a broad an integrated perspective is often necessary. Integrated Marketing Communication a. Relationship Marketing has aim to build mutually satisfying long-term relationship with key parties like customers, suppliers, distributors etc. for making a strong marketing network. b. Integrated Marketing Activities to create, communicate and deliver value to customers through diversified set of integrated activities eg. 4 P’s of Marketing, communication mix, offering mix etc. c. Internal Marketing It ensures that every one in the organization embraces appropriate marketing functions like sales force, advertising, customer service, product management, marketing research, hiring, pricing etc. d. Social Responsibility Marketing Understanding social, ethical, environmental & legal concern of society. Marketing Functions: Five Classics Functions and a Forgotten One Contact : Seeking out of prospective customers. Merchandising: Bring the right products to the right place at right time in the right quantity at the right price. Pricing: Determining factor when a purchase is made and a key to profit Marketing Functions: Five Classics Functions and a Forgotten One Promotion: Convincing customers through ads, personal selling, pr and other efforts. Distribution: The process of putting the customer and the product together. Human Resources: Transactions don’t take place between companies and faceless consumers but between flesh-and-blood human beings. Else is what? You can download this presentation by today 9 pm from www.bbs.autov.com.cn