* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 Chapter 21 - Darwin
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
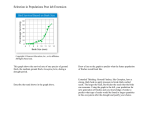
The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of life “Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution." -- Theodosius Dobzhansky March 1973 Genet icist , Columbia U niversit y (1900-1975) 2006-2007 Darwin: Historical Man of Mystery Plato & Aristotle (427 – 342 B.C.) Ideal organisms already adapted perfectly to environment, so no evolution Natural Theology (1700s) Creator specifically designed all organisms Carolus Linnaeus created taxonomic system to discover God’s order Georges Cuvier (1769-1832) Succession of fossils in sedimentary rock – throughout layers, species appear & disappear Believed in catastrophism – due to massive changes of environment James Hutton (1726-1797) – gradualism – little changes add up Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1700s) Use & disuse (use creates strength, disuse creates weakness) Inheritance of acquired characteristics (pass those strengths to offspring – ex:giraffe neck) Lamarck’s major contributions – Evolution explains fossil record & current diversity Organisms adapt to environment The man, the legend, the icon!! 1809-1882 22 years old – HMS Beagle – on board as “conversation companion” to captain Voyage to chart coastline of S.A. Darwin interested in geographic distribution of species, similarities, & differences on Galapagos islands Warbler finch Cactus finch Woodpecker finch Sharp-beaked finch Small insectivorous tree finch Small ground finch Cactus eater Medium ground finch Insect eaters Seed eaters Bud eater Large ground finch Seed eaters Flower eaters Insect eaters Finches were studied – very different from island to island Beaks have “adapted” to environment (food source/location) Natural selection – driving force of evolution (“Descent with Modification”) Biological diversity – product of evolution (a) Cactus eater. The long, sharp beak of the cactus ground finch (Geospiza scandens) helps it tear and eat cactus flowers and pulp. (c) Seed eater. The large ground finch (Geospiza magnirostris) has a large beak adapted for cracking seeds that fall from plants to the ground. (b) Insect eater. The green warbler finch (Certhidea olivacea) uses its narrow, pointed beak to grasp insects. Unity of life explained by common ancestor As life progressed, accumulation of diverse modifications diversity of today Link to Linnaeus – more taxonomic levels in common, more recent shared ancestor Differential success in reproduction Interaction between environment & inherited variety of individuals within a population Product is adaptation of populations of organisms to their environment Differential Success in Reproduction Environmental interaction Ex: Peppered Moth Industrial melanism Prior to Industrial Revolution After the Industrial Revolution Antibiotic/chemical resistance Drug Resistant HIV Note: in another environment, these characteristics might be considered detrimental, but in this environment, they are a benefit for these organisms. Homology - similarity of characteristics from common ancestor Homologous anatomical structures - Same structure, different function Remember….homologous (common ancestor) NOT analogous (similar function, different structure) Spines are homologous Remember….homologous (common ancestor) NOT analogous (similar function, different structure) Vestigial structures can help explain link between organisms Hip bones -snake Pelvic bones – whales Human appendix Biogeography (geographic distribution of species) Biogeography of the Draco lineatus complex (the Lined Flying Lizard) Convergent evolution Evolutionary change due to similar environmental pressures, not a recent common ancestor marsupial mammals placental mammals Convergent evolution Fossil Record 550 500 Body size (kg) 450 Equus 400 350 300 250 Merychippus 200 150 Mesohippus Hyracotherium 100 50 Nannippus 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Millions of years ago Fossils can be dated by variety of methods Age of rocks where fossil is found Isotope decay rate (carbon-14) Phylogenetic trees Mathematical calculations from chemical properties or geographical data Artificial Selection Influencing breeding based on desired traits