* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creationism wikipedia , lookup
Scopes Trial wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation–evolution controversy wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Mormon views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
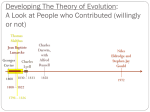
Chronology of Evolution Theory Curriculum Outcomes Students will be expected to: Describe historical and cultural contexts that have changed evolutionary concepts (316-1) Describe the importance of peer review in the development of evolutionary knowledge (114-5) Explain how knowledge of evolution evolves as new evidence comes to light and as laws and theories are tested and subsequently restricted, revised, or replaced (115-7) Theories About the Origin of Life Three possible ways that life could have come into existence: A. B. C. Random, natural unguided forces or processes Designed and created by a designer Self-generation or ability to create, inherent or designed into matter. Judeo-Christian-Islamic Tradition God created Earth and Heaven Separated light from dark/sea from sky Created plants and animals Created “mankind” Scientific Perspective Present universe created from “Big Bang” Earth coalesced from projected material Vulcanism of Earth’s crust created atmosphere and oceans Producers then consumers developed through a set of random chemical interactions Gradual, random change in genetic chemistry that improved survivability caused the evolution of organisms HISTORY OF THEORIES ABOUT THE ORIGINS OF LIFE History of Biology/Evolution Xenophanes (570-475 BCE) Greek philosopher, poet, religious and social critic Examined fossils Plato (427-347 BCE) Plato was a student of Socrates 345 B.P. Plato's Theory of Forms said all life forms represent an imperfect replica of a perfect heavenly model. Speusippus (408-339 BCE) wrote books on biological classification before Aristotle Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) is known as an artist but was also an anatomist. He dissected hundreds of specimens and drew exact copies of them Conrad Gessner (1516-1565) his three-volume Historia Animalium is considered the beginning of modern zoology Archbishop James Ussher Born January 4, 1581 Archbishop of Armagh 1650 - “Annales veteris testamenti, a prima mundi origine deducti” Creation on evening of October 23, 4004 BC Died March 21, 1656 Marcello Malpighi (1628-1694) was an Italian doctor, who gave his name to several physiological features. He was pioneer in using a microscope and he has also been described as a founder of comparative physiology and microscopic anatomy. Robert Hooke (1635-1703) coined the biological term “cell” Comte de Buffon Born September 7, 1707 1750 - Histoire naturelle, générale et particulière Living creatures evolve according to natural laws Hypothesized that the “creation of species” did not occur in one single place; Suggests humans and apes related!!! Died April 16, 1788 Pierre Louis de Maupertuis French mathematician One of earliest scholars to propose a rudimentary explanation of evolution 1751 wrote: “ the multiplication of species was a result of accidental recombination of elementary particles leading to offspring that differed from their ancestral forms.” Carol Linnaeus Swedish botanist 1760 raised Buffon’s unorthodox viewpoint Founder of binomial nomenclature (system of naming organisms based on physical features) His work of organizing the biological world into kingdoms, families, species, etc. is still being used today. Because of his work, scientists today can refer to an animal by a specific name and it is understood worldwide. Erasmus Darwin Born December 12, 1731 Charles Darwin’s grandfather 1794 – Zoonomia - attempted to explain organic life according to evolutionary principles. First true ‘evolutionist’ “Would it be too bold to imagine ... that all warm-blooded animals have arisen from one-living filament?" Died April 18, 1802 Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) coined the term “biology” and taught that evolution functions by inheritance of acquired characteristics 1809 - Philosophie Zoologique presented a comprehensive theory of transformism. Charles Lyell 1830 First volume of Charles Lyell's Principles of Geology interprets earth history as a process of gradual change. Lyell felt that geological processes are so uniform that their rates and effects must balance out through time. Processes that build mountains must eventually be balanced by the erosion of those mountains. Charles Darwin Born February 12, 1809 Voyage on the HMS Beagle (Dec., 1831 - Oct., 1836) Galapagos Islands – Darwin’s finches 1859 - “On the Origin of Species” Theory of Natural Selection Died April 19, 1882 Alfred R. Wallace 1858 Alfred R. Wallace proposed, in a letter to Charles Darwin, a theory of evolution by means of natural selection based on his work in Indonesia. The two agreed to present their papers on the same occasion to the Linnean Society. The Tipping Point 1859 Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species; or, The Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. Darwin’s Finches Thomas Henry Huxley 1863 Thomas Henry Huxley's Man's Place in Nature stressed the similarities between humans and apes. 1863 Lyell's Antiquity of Man popularized the belief that the human race is much older than allowed by the biblical time scale. Spontaneous Generation In the early 1600’s and before, it was believed that living organisms arose from the environment like dust and dirt There were many attempts to disprove this theory, a feat successfully achieved by Louis Pasteur in 1864 Pasteur’s Experiment Gregor Mendel Born July 22, 1822 1865- Suggests that traits are passed on through generations Published the results of his investigations of the inheritance of "factors" in pea plants. Died January 6, 1884 Around the same time, scientists start to accept Darwin’s theory of evolution Antoine Henri Becquerel Physicist credited with the discovery of radioactivity 1896 – Uses radioactive dating to show that the Earth is ~ 4.3 billion years old G. H. Hardy and W. Weinberg 1908 - recognized that evolutionary change is not automatic, that it occurs only when something disturbs the genetic equilibrium. Alfred Wegener 1912 - a geophysicist proposed the theory of continental drift and an earlier supercontinent called Pangaea, which split to form the current continents. William Jennings Bryan Born March 19, 1860 1920 – American politician launches anti-evolution campaign ‘The Menace of Darwinism’ speech 1923 - Oklahoma & Florida pass laws banning teaching evolution Died July 26, 1925 The Scopes Monkey Trial After the Tennessee legislature passed its anti-evolution law in March 1925, the American Civil Liberties Union advertised for a test subject, and a Dayton teacher named John Scopes volunteered to be the defendant. Scopes was a physics teacher who had occasionally taught biology as a substitute; he could not specifically remember mentioning evolution to his students, but he thought he probably had at some point. A fellow opponent of the law from Dayton swore out the complaint against him. Scopes The legal issue was somewhat beside the point -- whether Scopes broke the antievolution law. The judge easily found that he did, and fined him $100. The Scopes trial did not go beyond Tennessee but the evolution versus creation, science versus religion debate raged on. Proof of Evolution’s Mechanism 1953 J. D. Watson and F. H. C. Crick published the structure for DNA in Nature. Genesis Flood Published in 1961 Beginning of “young earth creation” Suggests that the Earth is not millions of years old, as evolutionists (and even most anti-evolutionists) believe Supreme Court 1968 Susan Epperson vs. Arkansas Challenges Arkansas law banning teaching of evolution in schools Supreme Court rules law unconstitutional, essentially striking down all laws banning the teaching of evolution The court ruled that evolution can be taught in public schools because it is a science, but not creationism, because it constitutes religion Donald Johansson 1974 - Discovered fossilized human relative 4 million years old Named it Lucy – Australopithecus afarensis Ape sized brain, but walked upright 1990's The human genome project was begun. Pope John Paul II Born May 18, 1920 Real name: Karol Józef Wojtyła 1996 - Endorses evolution, building on Pope Pius XII Accepts that scientific proof for evolution can not be ignored Different fields, many researchers Died April 2, 2005 “The convergence, neither sought nor fabricated, of the results of work that was conducted independently is in itself a significant argument in favor of this theory." USA Evolution Challenges 1999 – Columbine School shootings prompt politicians to blame lack of morals in youth on teaching of evolution 2000 – Students at Jefferson High in Lafayette, Ind. Petition to have creation taught in biology classes What do we know so far? The Wall of Time The Big Bang Theory video clip What You Oughta Know Thinking Critically Resource: Biologists