* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
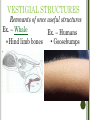
EVOLUTION “It is not the strongest of the species that survives, nor the most intelligent that survives. It is the one that is the most adaptable to change.” ~Charles Darwin EVOLUTION Change in a species’ genetic makeup over time Theory (well tested explanation) Charles Darwin BEFORE DARWIN… Inheritance of Acquired Traits (Jean Baptiste Lamarck) Organisms acquired or lost traits based on use during its lifetime & passed to offspring BEAGLE (1831) Collected specimens & fossils around the world GALAPAGOS ISLANDS • Observed many organisms • • High number of endemic species (species found only there) 97% of island is protected GALAPAGOS ISLAND SPECIES OF INTEREST 1859 – ORIGIN OF SPECIES Before DNA Introduced Artificial selection Natural selection Evolution ARTIFICIAL SELECTION Nature provides variation, humans select variations that are useful. Examples: • Farmers breeding best livestock • Domesticated dogs NATURAL SELECTION The traits that help an organism survive in a particular environment are “selected” for in nature STEPS IN NATURAL SELECTION 1. Genetic variation Difference in color, size, etc. Genetic mutation (after Darwin) 2. Over 3. population Struggle to survive Not 4. enough resources Successful reproduction Well adapted live and reproduce Adaptation Video EUROPEAN PEPPERED MOTHS • • • Rested on tree trunks Moths rest with their wings folded down Birds were predators EUROPEAN PEPPERED MOTHS Two color variations Dark Pale Before Pale By 1850 more common 1860 Dark more common WHAT HAPPENED IN THE 1850S? Trees covered in lichens Pale: blended Dark: stood out 1850s – Industry Soot covered trees Dark: blended Pale: stood out Simulation NATURAL SELECTION TO EVOLUTION • Insecticides – chemicals used to rid plants of unwanted insects • Antibiotics – treat bacterial infections • Work well before = now ineffective Why? Resistance SUMMARY OF DARWIN’S THEORY 1. Organisms differ; variation is inherited 2. Organisms produce more offspring than survive 3. Organisms compete for resources 4. Organisms with advantages survive to pass those advantages to their children 5. Species alive today are descended with modifications from common ancestors TWO TYPES OF EVOLUTION 1. Divergent – related species become more dissimilar 2. Convergent – unrelated species become more similar in appearance as they adapt to a similar environment EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION Fossil Record Homologous structures DNA Embryonic structures FOSSIL RECORD Fossils changed between different layers of the earth Youngest Oldest HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES Structures with different mature forms that develop from the same embryonic tissue Modified for specific function ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES Similar form & function, but are structurally quite different Same habitat DNA Common ancestors =common DNA Greater # of DNA similarities = closely related EMBRYONIC STRUCTURES Embryos may look more similar to adults All vertebrates look similar as embryos VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES Remnants of once useful structures Ex. – Whale Ex. – Humans Hind limb bones • Goosebumps Speciation Geographic Isolation Changes leading to formation of new species. Populations evolve and become reproductively isolated from each other(members of two populations cannot interbreed) Behavioral isolation