* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH 17 Taxonomy TErev07v22013
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
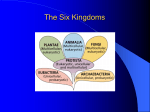
Taxonomy TAXONOMY: the science of classification Classificationthe grouping of objects or information based on similarities. ARISTOTLE (384-322 B.C.) First taxonomist (“Father of Classification”) “Mine is the first step and therefore a small one, though worked out with much thought and hard labor. You, my readers or hearers of my lectures, if you think I have done as much as can fairly be expected of an initial start … will acknowledge what I have achieved and will pardon what I have left for others to accomplish.” Aristotle created: TWO KINGDOMS PLANTS ANIMALS Herbs On Land Shrubs In the Air Trees In Water Carolus Linnaeus / Carl von Linne` The Father of Modern Taxonomy 1707-1778 BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE Two word naming system Genus - first word Species - second word Describes a characteristic of the organism Latin is the language used (some Greek) (Also called “Linneaus’s system”) LEVELS OF CLASSIFICATION: KINGDOM PHYLUM “Species”: organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring CLASS 0RDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES HOW ORGANISMS ARE CLASSIFIED: STRUCTURAL SIMILARITIES BREEDING BEHAVIOR CHROMOSOME BIOCHEMISTRY COMPARISONS SIMILAR DNA CLADISTICS (cladogram) MODE OF NUTRITION GEOGRAPHIC LOCATION PHYLOGENY PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE Theory of Evolution: the change in populations over time Charles Darwin (1809 – 1882) Proposed that species changed over time by natural selection Natural selection – organisms with traits suited to their environment survive and reproduce at a greater rate than others less suited Homologous structures – similar structures of common ancestors Research was conducted on the Galapagos Islands Natural Selection: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R6La6_kIr9g THE SIX KINGDOMS OF LIFE PLANTS ANIMALS FUNGI PROTISTS EUBACTERIA ARCHAEBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA Unicellular Prokaryotes Cell walls Reproduce asexually (binary fission) and/or sexually (conjugation) Live in extreme habitats: 1. Oxygen-free (Methanogens) 2. Salty brines (Halophiles) 3. Hot, acidic H20 (Acidophiles) KINGDOM EUBACTERIA Unicellular Prokaryotes Cell walls Binary fission and/or conjugation Some are: 1. Parasites 2. Saprophytes (saprobes) 3. Autotrophs Live everywhere KINGDOM PROTISTA Unicellular or multicellular Eukaryotes Heterotrophs (protozoans) and/or autotrophs (algae) Plantlike (algae), animallike (protozoans) or funguslike Sexual and/or asexual reproduction Found in aquatic habitats KINGDOM FUNGI Multicellular (most) Eukaryotes Absorptive heterotrophs (extracellular digestion) Cell walls (made of chitin) Sexual and/or asexual reproduction – by spores Found in damp, dark environments KINGDOM PLANTAE Multicellular Eukaryotes Autotrophs/ photosynthesis Cell walls (made of cellulose) Sexual reproduction (most) by seeds or spores Found on all types of land KINGDOM ANIMALIA Multicellular Eukaryotes Ingestive heterotrophs Cell membranes Specialized cells Sexual reproduction (most) by eggs & sperm Found everywhere THE END!