* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic: Evolution
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
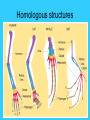
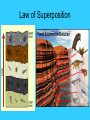
Topic: Evolution Aim: How did life evolve on Earth? When did the Earth form? • 4.6 billion years ago • Atmosphere: (air) little O2, mostly poisonous chemicals • Oceans: “soup” all different chemicals How did cells form? • Chemicals in the ocean combined → • Formed the building blocks of life → • CELLS (3.5 billion years ago) What did the first cells look like? 1. Anaerobic: no oxygen needed; heterotrophs evolved 2. Cells that carry out photosynthesis; autotrophs evolved 3. Aerobic: uses oxygen evolved 4. Multicellular organisms Topic: Evolution Aim: How do fossils support the theory of evolution? Do Now: Read the article. How does the article relate to evolution? What is your reaction to the article? What is evolution? • Change in a species over time • Species: group of organisms that share similar characteristics and can interbreed with one another to produce offspring • Geologic time scale: calander of Earth’s history • PRECAMBRIAN – first 4 billion years (few fossils) What evidence is there for evolution? • • • Fossils: remains/evidence of a living thing (bones, shells….) Fossils form when organisms die → get buried in sediments (particles of soil and rock) Some fossils become petrified – remains change into rock What is the fossil record? • All the fossils scientists have collected • Most complete biological record of life on Earth * Evidence that generations of species go through changes * What is an adaptation? • Change that increases an organism’s chances of survival • May be caused by a mutation Topic: Evolution Aim: What other pieces of evidence besides fossils support the theory of evolution? Evidence of Evolution 1. Fossils 2. Anatomical evidence • Homologous structures: body parts from different organisms are similar in structure (shape and arrangement) • Examples: human arm Suggest that all bat’s wing evolved from a whale’s flipper common ancestor dog’s leg Homologous structures Evidence of Evolution 3. Embryological evidence • Embryos of vertebrates are very similar suggesting that they are closely related (common ancestor) Embryological evidence Evidence of Evolution 4. Chemical evidence • Similarities in DNA suggests closely related organisms 5. Molecular evidence • Similarities in the structure of proteins suggests closely related organisms What do all of these various types of evidence tell us? • LIVING THINGS HAVE DESCENDED (EVOLVED) FROM A COMMON ANCESTOR!!! Topic: Evolution Aim: How can the age of fossils be determined? How can the age of fossils be determined? 1. Absolute dating (radioactive decay) • Determines actual age • Rocks that fossils are found in contain radioactive elements • Half-life analysis determine age of rock How can the age of fossils be determined? 2. Relative dating • Which of 2 fossils is older? • Sedimentary rock: layers of sediments that pile up on top of each other over time (may contain fossils) • Law of Superposition: younger rocks/fossils lie on top of older rocks/fossils (young fossils → top layers old fossils → lower layers) Law of Superposition Law of Superposition 1. Which layer is the I youngest? 2. Which layer is the oldest? A 3. Which is older layer C or F? Why? C – lower layer 4. A fossil found in layer G would be Older ______ than a fossil found in layer I. Who is Charles Darwin? • Explored/observed the Galapagos Islands • Book: On the Origin of Species • NATURAL SELECTION – idea used to explain how evolution occurs What is natural selection? • Survival & reproduction of those organisms best adapted to their surroundings Causes of Natural Selection 1. OVERPRODUCTION • Overproduction: when a species produces more offspring than can be supported by the environment • Results in competition • “Survival of the Fittest”: only the bestadapted members of a species survive (nature selects the fittest = natural selection) Causes of Natural Selection 2. VARIATIONS • Variations: differences between organisms of the same species that will allow them to adapt and survive • May be caused by mutations Summary: Natural selection is based on the two ideas – OVERPRODUCTION & VARIATION How long does it take evolution to occur? • Two theories 1. PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM • Evolution occurs in rapid and sudden changes in a species after a long period of little or no change (usually after a mass extinction) How long does it take evolution to occur? 2. GRADUALISM • Evolution occurs gradually over time Comparison: Punctuated Equilibrium & Gradualism Gradualism Punctuated Equilibrium ***Both theories seemed to have occurred during Earth’s History***