* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
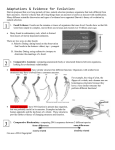
Evolution • Evolution – populations change over time • Current theory – life forms have descended from previous forms through changes in structure/function. Example often cited: horse feet. • Occurs SLOWLY Cited Evidence • Fossils – evolutionists say that organisms have become more complex over time • Homologous structures – those that have similar structures but different functions (bird wing compared to human arm and whale flipper) – evolutions say this is evidence of descent from a common ancestor • Vestigial organs – those that serve no function. Examples cited – human tail bone and appendix. Evolutionists say this is evidence of organs in an ancestor which lost their function. Darwin’s Finches • The beaks are different shapes – corresponding to different feeding habits Theories of Evolution • Lamark – acquired characteristics (giraffe necks) – WRONG • Darwin – Natural Selection: – Organisms have natural variation (from mutations) – Those organisms better able to compete survive to reproduce – AKA survival of the fittest – Most used example: peppered moth – ****Does NOT change an individual organism!!!! Important Terms • Mutation: change in DNA • Natural Selection: change in gene frequencies as a result of differences in survival and reproduction among organisms • Gene Flow: Change in the genetic traits as organisms enter or leave a population • Genetic Drift: Random changes in gene frequencies over time Adaptations • Adaptation: an inherited characteristic that makes a species more suited to its environment (examples – tortoises; rabbits) • NOT changes in an individual organism • Instead, changes in the # of individuals that have the particular trait Remember • Survival of the fittest means that POPULATIONS evolve – NOT INDIVIDUAL ORGANISMS Geographic Isolation • Geographic isolation occurs when a population becomes separated by changes in the environment • Example – changes in a river’s course, ponds in Death Valley Convergent Evolution • Adaptations of different species that make them more alike. • Common in animals in similar environments • Example: shape/fins of sharks, penguins and porpoises. Divergent Evolution • When organisms of the same species develop adaptations that make them more different. • Common when separated into different environments. • If many adaptations occur, new species are developed. • Example: many species of birds from a common ancestor Extinction • Occurs when there is a sudden change in the environment with no time for adaptations • Asteroids, habitat destruction, overhunting Biodiversity • All the different life forms on the planet: The sum of all the genetic material of all organisms • All ecosystems, all species, with all their DNA • Biodiversity is reduced when man alters environments (over killing, pollution, kudzu) The Fossil Record • Fossil – any evidence of an organism left behind • Examples: bones, molds (i.e. footprints) • Fossilization begins when an organism is suddenly buried (volcano, for example). As sediments pile up over time, organism’s remains are transformed into a fossil Fossil Terms • Paleontology – the study of fossils • Stratification – layers of sedimentary rock. Different fossils are found in different layers • Fossils are dated by relative dating. The fossils themselves are not dated, but are considered older/younger based on which layer of rock they are found in. Absolute Dating • Radioactive Dating: – C-14 is present in all living things – Half life is 5700 years. Geologic Record • Evolutionists say that the earth is more than 4 billion years old, and that humans have existed for only a few hundred thousand years. • So how do they come up with what was going on billions of years ago? • Their key concept: uniformity – all geological processes going on now (faulting, erosion, etc) were also going on in the past.